In color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, hue is one of the main properties of a color, defining its dominant wavelength. This characteristic determines whether we perceive a color as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or violet. Understanding hue is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color.

Defining Hue
- Definition: Hue is the degree to which a color can be described as similar to or different from the primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More red, yellow, and blue.
- Representation: Quantitatively, hue can be represented by a single number, often corresponding to an angular position on a color wheel.
Colors with the same hue can vary in lightness and colorfulness, such as “light blue,” “pastel blue,” “vivid blue,” and “cobalt blue.” Brown, for example, is a dark orange.
Hue in Color Models
Hue plays a crucial role in various color models used in digital and print media.
- RGB Model: In digital screens, the RGB model uses red, green, and blue to create different hues by varying their intensities.
- CMYK Model: In print, the CMYK model uses cyan, magenta, yellow, and black to produce a full spectrum of hues.
- Hex Codes: Web design uses hex codes, a six-digit combination representing RGB values, to specify hues.

Psychological and Cultural Significance of Hue
Hues have different psychological impacts and cultural meanings.
- Red: Often associated with passion and excitement. In some cultures, it symbolizes luck and prosperity.
- Blue: Conveys calmness and stability. Commonly used in corporate branding for its professional appeal.
- Green: Represents nature and health. Frequently used in environmental and health-related contexts.
- Yellow: Evokes happiness and energy. Also used to signify caution.
Deriving a Hue
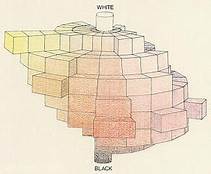
The concept of a color system with hues dates back to 1830 with Philipp Otto Runge’s color sphere. The Munsell color system, developed in the 1930s, advanced this idea by creating a perceptually uniform color space.
- Munsell Color System: This system organizes colors based on three properties: hue, valueIn color theory, value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. This concept is crucial for artists and designers because it helps create depth, contrast, and visual interest in their work. Value is one of the three properties of color, alongside hue and saturation. Defining Value Value indicates how light or dark a color appears. It ranges from More (lightness), and chroma (colorfulness).
- Conventions: In most color spaces, the hue for red is set to 0°.
Hue in Opponent Color Spaces
In opponent color spaces, hue is computed along with chroma by converting coordinates from rectangular to polar form.
- CIELAB and CIELUV: These color spaces use the angular component of the polar representation to determine hue.
- Formulas: In CIELAB, hue is calculated using atan2(b*, a*), while in CIELUV, it uses atan2(v*, u*).
Defining Hue in Terms of RGB
Hue can also be derived from the RGB color model using a polar plot or color hexagon. The hue angle is calculated based on the positions of red, green, and blue in the color space.

Usage in Art
In paintingPainting is a fundamental form of visual art that has been practiced for thousands of years. It involves applying pigment to a surface such as canvas, paper, or a wall. Painting can be explored through various styles, techniques, and mediums, each offering unique possibilities for expression and creativity. Historical Background • Ancient Beginnings: The history of painting dates back to More, hue refers to a pure pigment without any tintIn color theory, a tint is a lighter version of a color, created by adding white to the original hue. This simple yet powerful concept is fundamental for artists and designers, as it allows for a wide range of lighter tones that can be used to create depth, contrast, and visual interest in a composition. Defining Tint A tint results More (added white) or shade (added black). Manufacturers often label colors with “hue” to indicate safer or cheaper alternatives to toxic pigmentsPigments are essential to the creation of art, providing the vibrant colors that artists use to bring their visions to life. These substances, derived from a variety of natural and synthetic sources, have a rich history and a wide range of applications in both traditional and modern art. Colour Pigments Definition and Composition • Pigment: A material that imparts color More while maintaining the original hue.
Hue vs. Dominant Wavelength
Dominant wavelength is a physical analog to the perceptual attribute of hue. It is determined by drawingDrawing is a foundational art form that involves creating images on a surface, typically paper, using tools such as pencils, pens, and charcoal. It is a versatile medium that allows artists to express ideas, emotions, and stories through lines, shapes, and shading. Historical Background • Prehistoric Beginnings: The earliest known drawings date back to prehistoric times, with cave drawings found More a line from a white point through the color’s coordinates on a chromaticity diagram until it intersects the spectral locus. The intersection point identifies the color’s dominant wavelength.
Hue Difference Notation
Two main methods quantify hue difference. The first is the simple difference between two hue angles, denoted as Δhab in CIELAB and Δhuv in CIELUV. The second is the residual total color difference after accounting for lightness and chroma differences, symbolized as ΔHab* in CIELAB and ΔHuv* in CIELUV.
Names and Other Notations
There is some correspondence between hue values and color names. Traditional color terms are often used with more precise definitions. Alternative systematic notations include angle notations for color models like HSL/HSV, CIELUV, and CIECAM02. Alphanumeric systems like the Munsell color system, NCS, and Pantone Matching System are also common.
