Tobias Mayer (1723–1762) was a German astronomer, cartographer, and mathematician known for his work in color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More and lunar mapping. Despite his short life, Mayer made significant contributions that influenced later scientific and artistic developments.
Born in Marbach am Neckar, Mayer displayed a talent for mathematics and science from an early age. He held various academic positions and contributed to multiple fields, including astronomy and color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More.

- Key Contributions:
- Developed a color triangle
- Advanced the study of lunar motion and cartography
- Worked on navigation and geodesy
Color Triangle: Mayer’s most notable contribution to color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More is his color triangle, which he introduced in 1758. This diagram aimed to represent colors systematically and was an early attempt to understand color relationships and mixing.
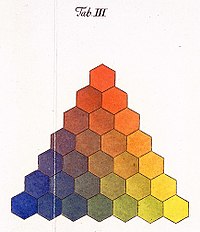
- Color Relationships:
- Developed a triangular color diagram
- Showed how primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More mix to form secondary colorsSecondary colors are a fundamental aspect of color theory, created by mixing two primary colors in equal measure. The three secondary colors are green, orange, and purple. These colors expand the palette available to artists and designers, allowing for a broader range of hues and shades in their work. Understanding secondary colors is essential for anyone looking to deepen their More
- Illustrated the gradation and blending of colors
The color triangle placed the primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More (red, yellow, and blue) at its vertices and secondary colorsSecondary colors are a fundamental aspect of color theory, created by mixing two primary colors in equal measure. The three secondary colors are green, orange, and purple. These colors expand the palette available to artists and designers, allowing for a broader range of hues and shades in their work. Understanding secondary colors is essential for anyone looking to deepen their More (orange, green, and violet) along its edges. It demonstrated how intermediate colors can be created by mixing these primary and secondary colorsSecondary colors are a fundamental aspect of color theory, created by mixing two primary colors in equal measure. The three secondary colors are green, orange, and purple. These colors expand the palette available to artists and designers, allowing for a broader range of hues and shades in their work. Understanding secondary colors is essential for anyone looking to deepen their More.
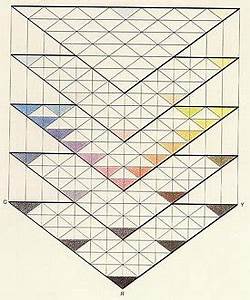
Color Perception: Mayer was interested in how humans perceive colors and how different colors can be mixed to produce new hues. His work laid the groundwork for later developments in colorimetry and the scientific study of color.
- Human Perception:
- Studied how colors blend in human vision
- Investigated the creation of intermediate hues
- Laid foundations for modern colorimetry
His approach combined empirical observation with mathematical modeling, providing a bridge between artistic practices and scientific investigation.
Optical Observations: Mayer’s interest in optics extended beyond color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More. He also conducted experiments on light and vision, contributing to the broader field of optics. His work included studying the behavior of light and its interaction with different materials.
- Light Behavior:
- Conducted experiments on light and vision
- Studied reflection and refraction
- Contributed to the understanding of optical properties
His findings in optics were closely tied to his work in astronomy and navigation, where precise observations of light and celestial bodies were crucial.
Astronomy and Cartography: In addition to his work on color, Mayer made significant contributions to astronomy. He created detailed lunar maps and developed methods for predicting the moon’s position, which were essential for navigation.
- Lunar Mapping:
- Produced detailed maps of the moon
- Developed accurate lunar tables
- Improved methods for predicting lunar motion
His lunar tables were so precise that they were used by navigators to determine longitude at sea, significantly aiding maritime navigation.
Scientific Method: Mayer emphasized the importance of empirical data and mathematical precision in his research. His methodical approach to experiments and observations set a standard for future scientific work.
- Methodology:
- Combined empirical data with mathematical analysis
- Conducted systematic experiments
- Valued precision and reproducibility in research
This rigorous approach was evident in both his color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More and his astronomical work, highlighting his commitment to scientific accuracy.
Influence and Legacy: Mayer’s work in color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More influenced later scientists and artists. His color triangle concept was a precursor to more modern color models, and his methodologies in astronomy and navigation had lasting impacts.
- Impact:
- Influenced the development of colorimetry
- Provided tools for artists and scientists to understand color mixing
- His lunar tables and maps continued to be used for navigation
Tobias Mayer’s contributions, though cut short by his early death, remain influential. His work in color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More provided a systematic approach to understanding color relationships, blending artistic intuition with scientific rigor.
