- What is Color Theory?
- The History of Color Theory: The Context
- Color Theorists Through the Ages
- Aristotle (384 – 322 BCE)
- Hasan Ibn al-Haytham (965 – 1040 CE)
- Franciscus Aguilonius (1567 – 1617 CE)
- Isaac Newton (1642 – 1727 CE)
- Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749 – 1832 CE)
- Tobias Mayer (1723 – 1762)
- Philipp Otto Runge (1777 – 1810)
- Thomas Young (1773 – 1829 CE)
- Albert Henry Munsell (1858 – 1918 CE)
- Johannes Itten (1888 – 1967)
- Josef Albers (1888 – 1976)
- The Illusion of Primary Colors: Color Theory Today
- Primary Colors Depend on Device Type
- Human Experience of Color
- Final Thoughts
- Resources: Free Downloadables
- Recommended Readings: Best Books about Color Theory and Famous Color Theorists
- FAQ: Quick Answers
If you were asked to think of the color blue, what would come to mind?
Maybe it would be the feeling of relaxation, calmness, serenity, or a sense of stability and reliability. Or it might be the image of the ocean, a cloudless sky, or blue eyes looking at you, all floating through your head. Whatever it would be, most likely you linked the color to certain ideas, objects, and emotions. These spontaneous associations are a universal human experience, and they are widely used in art, design, psychology, marketing, and numerous other fields.
The psychology of color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More makes the study of color a powerful tool in the hands of creatives. To unleash the full power of color, it is helpful to understand both basic artistic and scientific concepts as well as the history of color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More.
What is Color TheoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More?
Color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More is the collection of guidelines and rules in the realm of art and science that explain how humans perceive and apply color. It is further the visual effects of how colors mix, contrast, and match with each other, involving the message colors communicate. To define color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, one must further refer to the color wheel and the differentiation between primary color, secondary color, and tertiary color.

The History of Color TheoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More: The Context
Humans invented the first pigments as early as 40,000 years ago. They combined soil, burnt charcoalCharcoal is a popular and expressive medium used in drawing. Known for its deep blacks and range of tones, charcoal allows artists to create dramatic and dynamic artworks with a distinct, textured look. Historical Background • Ancient Beginnings: Charcoal has been used since prehistoric times, with early humans using burnt sticks to create drawings on cave walls. These early works More, chalk, and animal fat to create a basic palette of five colors including yellow, red, brown, black, and white. Since then, colors, pigment theory, and theories of color have been subject to ongoing discovery both through artistic exploration and scientific advancement. Color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More in art and science has been advancing constantly.
How and why are humans able to perceive colours? Answers to this question have evolved over the centuries. Experts since ancient times have tried to decipher the composition of colors, challenged by grasping the technical workings and a modern understanding of colors theory.

For anyone occupied in the visual culture—artists, interior or graphic designers alike – the theory of colors and the science of color are essential elements of everyday work. This field of science encompasses the perception of colour by the human eye, the effects on the brain, art color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, the origin of colors, as well as the theory meaning of electromagnetic radiation.[1] From scientific to artistic, color and color perceptions have fascinated humans for centuries. Knowledge has been obtained from both a scientific and artistic viewpoint, while both areas combined gave rise to insights into our visual experience.
A basic understanding of the color spectrum and color scheme definition is easy to grasp, yet color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More is a highly complex subject, and it can be a daunting task to both satisfy the art historical and the scientific aspects of the issue. Artistic color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More is concerned with the visual effects of color combination, while scientific color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More describes the nature of color matters by using multifaceted color models. For a better understanding of color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, looking at the history of color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More as well as modern color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More is essential.

Color Theorists Through the Ages
AristotleAristotle (384–322 BCE) was an ancient Greek philosopher and polymath whose extensive work has influenced numerous fields, including science, philosophy, and art. His contributions to color theory, although not as widely known, were groundbreaking for his era. Aristotle's observations and theories laid the groundwork for future studies in color and vision. Aristotle was a student of Plato and the teacher More (384 – 322 BCE)
The first document about color theories originated in ancient Greece and was titled “On Colors”. For a long time, this color history text was attributed to AristotleAristotle (384–322 BCE) was an ancient Greek philosopher and polymath whose extensive work has influenced numerous fields, including science, philosophy, and art. His contributions to color theory, although not as widely known, were groundbreaking for his era. Aristotle's observations and theories laid the groundwork for future studies in color and vision. Aristotle was a student of Plato and the teacher More alone, yet it is nowadays broadly accepted that the AristotleAristotle (384–322 BCE) was an ancient Greek philosopher and polymath whose extensive work has influenced numerous fields, including science, philosophy, and art. His contributions to color theory, although not as widely known, were groundbreaking for his era. Aristotle's observations and theories laid the groundwork for future studies in color and vision. Aristotle was a student of Plato and the teacher More color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More was written by members of the Peripatetic School and the philosopher together, based on the color system they observed in nature around them.[2]
The document proposed that color was emitted by a deity through heavenly fire rays and that all colours were composed of brightness and darkness. It was believed that there were two basic primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More, blue and yellow, derived from darkness and light, which related to the binary system found elsewhere in the world, e.g., in the duality of day and night, male and female, or stimulus and sedation. Based on those two primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More, the Peripatetic School created a linear light theory of color which encompassed four further colors, ranging from the white light of noon to the black of the dark night.
The four other theory colors were found in between this range [3] and were thought to correspond to the four elements: green, red, yellow, and blue were matched with earth, fire, wind, and water respectively.
This concept might seem esoteric and speculative today, but it made sense at the time, standing in line with a general theory of how the universe operates. Notwithstanding, some observations by colour theorists of the Peripatetic school currently still have relevance, for example, the fact that darkness is not a colour but rather the absence of light.[4] This system was widely adopted by artists up until Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More replaced it with his general concept of color and the color wheel theory in 1672 (Hymann).

Learn more about AristotleAristotle (384–322 BCE) was an ancient Greek philosopher and polymath whose extensive work has influenced numerous fields, including science, philosophy, and art. His contributions to color theory, although not as widely known, were groundbreaking for his era. Aristotle's observations and theories laid the groundwork for future studies in color and vision. Aristotle was a student of Plato and the teacher More Color TheoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More here.
Hasan Ibn al-HaythamHasan Ibn al-Haytham (965–1040 CE), often known in the Western world as Alhazen, was a pioneering figure in the fields of optics, mathematics, and astronomy. His work laid the groundwork for many modern scientific principles, particularly in optics and color theory. Ibn al-Haytham was born in Basra, in present-day Iraq, and spent much of his life in Cairo. He made More (965 – 1040 CE)
While most ancient Greek philosophies revolved around theological means and reason, Hasan Ibn al-HaythamHasan Ibn al-Haytham (965–1040 CE), often known in the Western world as Alhazen, was a pioneering figure in the fields of optics, mathematics, and astronomy. His work laid the groundwork for many modern scientific principles, particularly in optics and color theory. Ibn al-Haytham was born in Basra, in present-day Iraq, and spent much of his life in Cairo. He made More was the first scientist in history who insisted that everything must be proven by means of scientific approaches. This meant that for his light and color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, he conducted experiments and had his hypotheses peer-reviewed.[5]
In “The Book of Optics”, the Middle Eastern scholar refuted the ancient Greek concept that light is emitted from the eye and reflected by objects back to the eye. His conclusion was that vision occurs once the light is given off the sun, a candle, other luminous sources, or a reflection into the eye. Experimenting with glass spheres filled with water, he concluded that light was refracted by the water at multiple angles to produce different colors of the rainbow. In his light color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, Ibn al-Haytham further provided evidence that the color and brightness of an object depended on the grade of brightness and surrounding colors.[6]
Many European scholars studied “The Book of Optik” by Ibn al-Haytham and recreated his experiments, which led to the usage of eyeglasses, telescopes, and cameras. Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More is the most famous color theorist to have used Ibn al-Haytham’s work but failed to reference him in his own writings.[7]

Learn more about Hasan Ibn al-HaythamHasan Ibn al-Haytham (965–1040 CE), often known in the Western world as Alhazen, was a pioneering figure in the fields of optics, mathematics, and astronomy. His work laid the groundwork for many modern scientific principles, particularly in optics and color theory. Ibn al-Haytham was born in Basra, in present-day Iraq, and spent much of his life in Cairo. He made More Color TheoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More here.
Franciscus AguiloniusFranciscus Aguilonius (1567–1617 CE) was a notable figure in the fields of optics and mathematics during the late Renaissance period. As a Jesuit scholar, his contributions significantly influenced the development of these sciences, particularly through his work on color theory and perspective. Born in Brussels, Aguilonius became a Jesuit in 1586 and later worked as a professor of mathematics at More (1567 – 1617 CE)
In the early 17th century, Belgian Jesuit Franciscus AguiloniusFranciscus Aguilonius (1567–1617 CE) was a notable figure in the fields of optics and mathematics during the late Renaissance period. As a Jesuit scholar, his contributions significantly influenced the development of these sciences, particularly through his work on color theory and perspective. Born in Brussels, Aguilonius became a Jesuit in 1586 and later worked as a professor of mathematics at More contradicted Aristotle’s binary color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More by formulating a color system based on three primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More (Hyman). While adhering to previous knowledge on the history of colours, e.g. keeping Aristotle’s two colors blue and yellow, he added red as a further primary color. This was the oldest system that included these three primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More, which are still used in theories of the primary color circle today.
Aguilonius was convinced that the noble primary hues of red, yellow, and blue could be derived from the two extremes of white and black as stated in his work “Optics in Six Chapters”. When mixing the primary hues, composite colors, later known as secondary color design, could be acquired – orange, purple, and green as part of his harmonious color list.
In his science of color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, Aguilonius considered white as pure and colors as gross matter, not yet understanding that light contained all colors of the spectrum and was not contaminated by gross matter. A further misconception was his light theory of color, stating that prisms were responsible for coloring the light, as opposed to the correct notion that color was composed of light.[8]

Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More (1642 – 1727 CE)
Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More completely redefined the theory of light and the history of colors when he first published his work “Optiks” in 1704. He had been familiar with the Latin translation of Al-Hasan Ibn al-Haytham’s texts and recreated several of the Middle Eastern scholar’s experiments. On this basis, Newton was able to prove that color was not composed of black and white but of white light alone.[9]
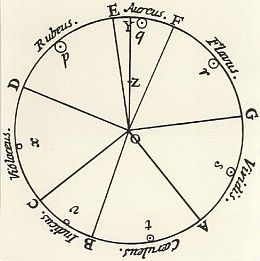
He further famously created the first color wheel, based on his observations of a glass prism producing a color spectrum ranging from red to violet. He came to the conclusion that the different colors were produced by various wavelengths and, in the tradition of AristotleAristotle (384–322 BCE) was an ancient Greek philosopher and polymath whose extensive work has influenced numerous fields, including science, philosophy, and art. His contributions to color theory, although not as widely known, were groundbreaking for his era. Aristotle's observations and theories laid the groundwork for future studies in color and vision. Aristotle was a student of Plato and the teacher More, selected seven hues. This concept brought an easy understanding of the color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More to the masses. Although Newton later found through experimentation that the rainbow is a continuous spectrum of color, he stuck to his seven-color concept.[10]
Rather than seeing white light as void of color, Newton further discovered that it was the combination of all colors across the color spectrum: When splitting the colors from across the spectrum, he was able to recombine these spectral colors to regain white light once again. When blending one color of the spectrum with another one, the result was a third color. Colors directly opposite of each other on the color wheel, such as red and green, canceled out each other’s hueIn color theory, hue is one of the main properties of a color, defining its dominant wavelength. This characteristic determines whether we perceive a color as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or violet. Understanding hue is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color. Defining Hue • Definition: Hue is the degree to which a color can be described More.[11]
Newton was the first to consider red, green, and blue as primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More. When combining blue and green light, the result was the color cyan, green, and red light mixed to give yellow, and red and blue light together had magenta appear. Based on these conclusions, Newton was able to create his color wheel in which the three primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More were separated by the three secondary colorsSecondary colors are a fundamental aspect of color theory, created by mixing two primary colors in equal measure. The three secondary colors are green, orange, and purple. These colors expand the palette available to artists and designers, allowing for a broader range of hues and shades in their work. Understanding secondary colors is essential for anyone looking to deepen their More yellow, cyan, and magenta.[12]

Learn more about Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More Color TheoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More here.
Johann Wolfgang von GoetheJohann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749–1832 CE) was a German writer, poet, scientist, and philosopher. He is best known for his literary works, but his contributions to the study of color were also groundbreaking and influential. Goethe's approach to color theory differed from the scientific perspective of his time, offering a more human-centered understanding of how we perceive color. His work, More (1749 – 1832 CE)
While Newton was solely interested in approaching color and light from a scientific viewpoint, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe’s color theory focused on the nature and the perception of colors. He dedicated his work “Theory of Colors”, first published in 1810, to a humanistic analysis and the connection between psychology and color theory.[13]

Goethe challenged Newton’s approach not only through his effective look at color matters. The German poet also believed that the prism, not the light, was responsible for the creation of color and disagreed further with Newton’s theory of color vision in which darkness was the absence of light. Instead, Goethe stuck to the ancient idea that color was composed through balancing light and darkness. He further applied Aristotle’s concept of blue and yellow as primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More, while blue was the color to come from darkness and yellow was the color to come from light.[14]
The experimental approaches for the theory of color of the scientist and the poet differed strongly. While Newton adhered to an additive theory of color using prisms and light, in his color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More Goethe used a subtractive approach mixing the pigmentsPigments are essential to the creation of art, providing the vibrant colors that artists use to bring their visions to life. These substances, derived from a variety of natural and synthetic sources, have a rich history and a wide range of applications in both traditional and modern art. Colour Pigments Definition and Composition • Pigment: A material that imparts color More of paints, which was more relevant to color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More in art. Goethe was convinced that in his subtractive color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, the three primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More could mix all visible colors including black: Combining paints of different colors would eventually result in a very dark tone by subtracting waves of light. Like Newton, Goethe presented his findings in a color wheel, but instead of red, green, and blue, Goethe’s color wheel included red, blue, and yellow as primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More and orange, violet, and green as secondary colorsSecondary colors are a fundamental aspect of color theory, created by mixing two primary colors in equal measure. The three secondary colors are green, orange, and purple. These colors expand the palette available to artists and designers, allowing for a broader range of hues and shades in their work. Understanding secondary colors is essential for anyone looking to deepen their More.[15]
Even though Newton’s notion eventually proved to be the correct one in many respects, Goethe’s color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More was significant since it focused on the cognitive effect of color on humans. Goethe strongly disagreed that color was simply a scientific field since personal experience had to be taken into account. This marked the beginning of the modernist study of the psychological impact of color and the psychological color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, which was welcomed by numberless artists.[16]

Learn more about Johann Wolfgang Goethe Color TheoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More here.
Tobias MayerTobias Mayer (1723–1762) was a German astronomer, cartographer, and mathematician known for his work in color theory and lunar mapping. Despite his short life, Mayer made significant contributions that influenced later scientific and artistic developments. Born in Marbach am Neckar, Mayer displayed a talent for mathematics and science from an early age. He held various academic positions and contributed to More (1723 – 1762)
German astronomer and mathematician Tobias MayerTobias Mayer (1723–1762) was a German astronomer, cartographer, and mathematician known for his work in color theory and lunar mapping. Despite his short life, Mayer made significant contributions that influenced later scientific and artistic developments. Born in Marbach am Neckar, Mayer displayed a talent for mathematics and science from an early age. He held various academic positions and contributed to More tried to create a unified notation for color with his color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More book “The Affinity of Color Commentary”, published posthumously in 1775. In his theory, colors were to be accurately defined according to how the human eye was able to perceive them. Consequently, he extended the analogous color wheel and invented a three-dimensional color triangle which also exemplified the variety of brightness for each color.
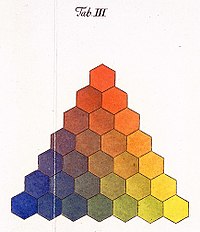
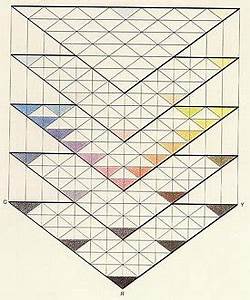
The corners of the triangle were kept in the three primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More known from paintingPainting is a fundamental form of visual art that has been practiced for thousands of years. It involves applying pigment to a surface such as canvas, paper, or a wall. Painting can be explored through various styles, techniques, and mediums, each offering unique possibilities for expression and creativity. Historical Background • Ancient Beginnings: The history of painting dates back to More – red, yellow, and blue, while the corners were connected by mixing the opposite colours. Then triangles of different brightness were arranged upon each other, which made the definition of a color by its position in a three-dimensional space and understanding color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More from a new angle possible.[17]

Philipp Otto RungePhilipp Otto Runge (1777–1810) was a German painter and draughtsman, widely recognized for his contributions to color theory and Romantic art. Despite his brief life, Runge's innovative ideas about color and his artistic vision left a lasting impact on the fields of art and color science. Born in Wolgast, Germany, Runge initially trained in commerce before pursuing his passion for More (1777 – 1810)
The German painter and draughtsman Philipp Otto Runge’s interest in color was a result of his occupation as an artist and a particular interest in science. He considered a similar approach to Tobias Mayer’s when creating his spherical representation of the color spectrum and published his artist color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More in the manuscript “Color Sphere” in 1810.

As indicated in one letter to Goethe, he expanded the color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More circle with the triadic colors yellow, red, and blue into a sphere, in which black and white formed two opposing poles. Between the poles, colored bands were arranged. Yet like numerous illustrations of color systems prior to his theory, his color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More chart did not distinguish between brightness and saturation, so that the scheme included only little variation regarding color concentration.[18]

Learn more about Philipp Otto RungePhilipp Otto Runge (1777–1810) was a German painter and draughtsman, widely recognized for his contributions to color theory and Romantic art. Despite his brief life, Runge's innovative ideas about color and his artistic vision left a lasting impact on the fields of art and color science. Born in Wolgast, Germany, Runge initially trained in commerce before pursuing his passion for More color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More here.
Thomas YoungThomas Young (1773–1829 CE) was an English polymath whose work spanned various fields, including physics, medicine, and Egyptology. His contributions to the study of light and color were particularly influential, laying the groundwork for modern wave theory and color vision. Born in Milverton, England, Young showed prodigious talents from a young age. He pursued studies in medicine but also made More (1773 – 1829 CE)
The British polymath Thomas YoungThomas Young (1773–1829 CE) was an English polymath whose work spanned various fields, including physics, medicine, and Egyptology. His contributions to the study of light and color were particularly influential, laying the groundwork for modern wave theory and color vision. Born in Milverton, England, Young showed prodigious talents from a young age. He pursued studies in medicine but also made More made notable contributions to the fields of light, vision, energy, and solid mechanics. The wave theory of light is attributed to him, contrasting the particle theory by Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More. Accordingly, Young has been called the founder of physiological optics and the color light theory, a field that is concerned with the perceptual processes in the eye.[19]
Through experimentation, Young proved that, unlike Newton’s theory, light was not a particle, but that light came in waves. He further hypothesized that it was possible to generate any color by mixing varying proportions of the three additive primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More of light, red, green, and blue. He further postulated that the human eye was only able to perceive the three primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More in fluctuating proportions, combining them internally to a larger variety of colors.[20]
On the basis of Young’s findings on how the primary color combination is perceived, the German physicist and physician Hermann von Helmholtz proposed that the human eye encompasses three kinds of cones or receptors in the retina. He therewith augured the modern concept of color vision that there are three nerve fibers in the eye that are sensitive to particular wavelengths of the spectrum visible. Depending on the degree of stimulation, the nerve fiber cones make objects appear in certain colors.[21]

Learn more about Thomas YoungThomas Young (1773–1829 CE) was an English polymath whose work spanned various fields, including physics, medicine, and Egyptology. His contributions to the study of light and color were particularly influential, laying the groundwork for modern wave theory and color vision. Born in Milverton, England, Young showed prodigious talents from a young age. He pursued studies in medicine but also made More color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More here.
Albert Henry MunsellAlbert Henry Munsell (1858–1918 CE) was an American painter, teacher, and the creator of the Munsell color system. His contributions to color theory and color science revolutionized the way colors are measured, categorized, and communicated, making a lasting impact on various industries, from art and design to manufacturing. Born in Boston, Massachusetts, Munsell trained as an artist at the Massachusetts More (1858 – 1918 CE)
The American artist Albert Henry MunsellAlbert Henry Munsell (1858–1918 CE) was an American painter, teacher, and the creator of the Munsell color system. His contributions to color theory and color science revolutionized the way colors are measured, categorized, and communicated, making a lasting impact on various industries, from art and design to manufacturing. Born in Boston, Massachusetts, Munsell trained as an artist at the Massachusetts More is famous for inventing a color combination theory named after him in the early 20th century, which was an early attempt to create an accurate system for numerically describing colors. Like scientists and artists before him, Munsell’s goal was to create a model displaying perceptually uniform steps, which was meant to serve as an accurate reference. Although starting from the perspective of an artist, his approach was exceptionally scientific, so he was the first one to combine the scientific color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More with the artistic one into a single theory to accurately identify every color that exists.[22]
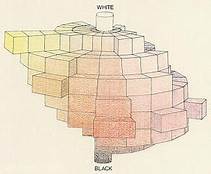
One major accomplishment of the Albert Munsell color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More was that it divided the color space into three dimensions, which had not been outlined before: The valueIn color theory, value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. This concept is crucial for artists and designers because it helps create depth, contrast, and visual interest in their work. Value is one of the three properties of color, alongside hue and saturation. Defining Value Value indicates how light or dark a color appears. It ranges from More defined the brightness of the color, the hueIn color theory, hue is one of the main properties of a color, defining its dominant wavelength. This characteristic determines whether we perceive a color as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or violet. Understanding hue is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color. Defining Hue • Definition: Hue is the degree to which a color can be described More determined the type of color (blue, green, etc.), while the chroma defined the saturation or purity of the color. As one moved up or down a line in a vertical direction, the valueIn color theory, value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. This concept is crucial for artists and designers because it helps create depth, contrast, and visual interest in their work. Value is one of the three properties of color, alongside hue and saturation. Defining Value Value indicates how light or dark a color appears. It ranges from More of the color either increased or decreased, while moving away from this vertical line, the saturation of the color changed. Hues changed when moving around the neutral line.
The Munsell color system achieved international acceptance since it allowed scientists to expand on it, as well as being simple enough for artists without a scientific background to apply it in their comparison of colors. It further proved to be a suitable colour theory for designers.[23]

Learn more about Albert Henry MunsellAlbert Henry Munsell (1858–1918 CE) was an American painter, teacher, and the creator of the Munsell color system. His contributions to color theory and color science revolutionized the way colors are measured, categorized, and communicated, making a lasting impact on various industries, from art and design to manufacturing. Born in Boston, Massachusetts, Munsell trained as an artist at the Massachusetts More color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More here.
Johannes IttenJohannes Itten (1888–1967) was a Swiss painter, designer, teacher, and one of the key figures of the Bauhaus school. Renowned for his work on color theory, Itten developed influential ideas that have shaped modern understanding and teaching of color in art and design. Born in Südern-Linden, Switzerland, Itten initially trained as a primary school teacher before pursuing his passion for More (1888 – 1967)
The Swiss expressionist painter, designer, and theorist Johannes Itten, like Goethe, believed that it was the subjective experience of color that mattered. In his color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, Itten was strongly influenced by his spiritual beliefs. His theoretical writings thus centered around how color could be combined to invoke feelings on the side of the viewer.
Itten’s contribution to the BauhausThe Bauhaus movement originated as a German school of the arts in the early 20th century. Founded by German architect Walter Gropius in 1919, the school was dedicated to uniting all branches of the arts under one roof. The Bauhaus acted as a hub for Europe's most experimental creatives, with well-known artist instructors like Wassily Kandinsky, Josef Albers, and Paul More color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More was the development of an innovative preliminary course, in which he taught students the basics of color and composition. He theorized seven types of color contrast including contrast by hueIn color theory, hue is one of the main properties of a color, defining its dominant wavelength. This characteristic determines whether we perceive a color as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or violet. Understanding hue is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color. Defining Hue • Definition: Hue is the degree to which a color can be described More, by valueIn color theory, value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. This concept is crucial for artists and designers because it helps create depth, contrast, and visual interest in their work. Value is one of the three properties of color, alongside hue and saturation. Defining Value Value indicates how light or dark a color appears. It ranges from More, temperature, complements, simultaneous contrast, contrast by saturation, and contrast by extension.[24] To explain these ideas, Itten used a color sphere with the primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More red, yellow, and blue, similar to the one invented by Runge.[25]
Johannes Itten’s color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, his concept about color interactions, and his color palettes directly influenced color abstraction movements and Op ArtOp Art, short for Optical Art, is a visual art movement that emerged in the 1960s, characterized by the use of geometric patterns, contrasting colors, and optical illusions to create a sense of movement or vibration. This art form plays with visual perception, engaging the viewer in dynamic and sometimes disorienting visual experiences. Origins and Development Op Art gained prominence More. He was further the first to associate color palettes with four types of people and labeled these types with the names of seasons. After his death, these designations gained traction in the cosmetics industry. His color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More in makeup and seasonal analysis is still highly popular today.[26]

Learn more about Johannes IttenJohannes Itten (1888–1967) was a Swiss painter, designer, teacher, and one of the key figures of the Bauhaus school. Renowned for his work on color theory, Itten developed influential ideas that have shaped modern understanding and teaching of color in art and design. Born in Südern-Linden, Switzerland, Itten initially trained as a primary school teacher before pursuing his passion for More color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More here.
Josef AlbersJosef Albers (1888–1976) was a German-American artist, educator, and influential figure in the fields of color theory and abstract art. Known for his profound impact on modern art education, Albers' work emphasized the perception and interaction of color. Born in Bottrop, Germany, Albers initially trained as a schoolteacher before pursuing his passion for art. He studied at the Bauhaus, where More (1888 – 1976)
The German artist and educator Josef AlbersJosef Albers (1888–1976) was a German-American artist, educator, and influential figure in the fields of color theory and abstract art. Known for his profound impact on modern art education, Albers' work emphasized the perception and interaction of color. Born in Bottrop, Germany, Albers initially trained as a schoolteacher before pursuing his passion for art. He studied at the Bauhaus, where More, a student Itten’s at the BauhausThe Bauhaus movement originated as a German school of the arts in the early 20th century. Founded by German architect Walter Gropius in 1919, the school was dedicated to uniting all branches of the arts under one roof. The Bauhaus acted as a hub for Europe's most experimental creatives, with well-known artist instructors like Wassily Kandinsky, Josef Albers, and Paul More, unlike his teacher, did not try to establish a unified theory about why color behaves a certain way. Instead, Josef Albers’ color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More was more demonstrative, and he exemplified the dynamic nature of color when teaching the basics of color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More and color paletteA color palette refers to a selection of colors used in design and art. It can set the tone, convey emotions, and highlight key elements. color wheel Types of Color Palettes • Monochromatic: Uses variations in lightness and saturation of a single color. Ideal for creating a harmonious and cohesive look. • Analogous: Combines colors that are next to each More theory.

In his book “The Interaction of Color” published in 1963, he showed that the human perception of colors was strongly influenced by the context of each color. The book includes a description of the primary, secondary, and tertiary color scheme, alongside a range of connotations that he assigned to specific hues on his triangular color model.[27]

Learn more about Josef AlbersJosef Albers (1888–1976) was a German-American artist, educator, and influential figure in the fields of color theory and abstract art. Known for his profound impact on modern art education, Albers' work emphasized the perception and interaction of color. Born in Bottrop, Germany, Albers initially trained as a schoolteacher before pursuing his passion for art. He studied at the Bauhaus, where More color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More here.
The Illusion of Primary ColorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More: Color TheoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More Today
As the history of color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More shows, there has been a lot of discussion about the nature of primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More. The reason is largely due to the confusion over subtractive color schemes and the additive theory of color. While in the art world, the three primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More are usually represented in a red-yellow-blue color wheel, in the world of physics, the three primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More are red, green, and blue.
Additive color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More mixing is understood to be the process of mixing the three physics primaries in different ways to create new hues. Each time a light source is added, the resulting color will be brighter and therefore closer to white. If all three colors are equally combined, the resulting color will be white. Subtractive color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More mixing on the other hand involves the three primaries from the art world: InkInk, a liquid or paste used for writing, drawing, and printing, has played a crucial role in communication and artistic expression throughout history. Made from various pigments and dyes, ink allows for the transfer of text and images onto surfaces such as paper, fabric, and other materials. Types of Ink There are several types of ink, each serving different purposes More or paint pigmentsPigments are essential to the creation of art, providing the vibrant colors that artists use to bring their visions to life. These substances, derived from a variety of natural and synthetic sources, have a rich history and a wide range of applications in both traditional and modern art. Colour Pigments Definition and Composition • Pigment: A material that imparts color More are combined to absorb or selectively transmit light.
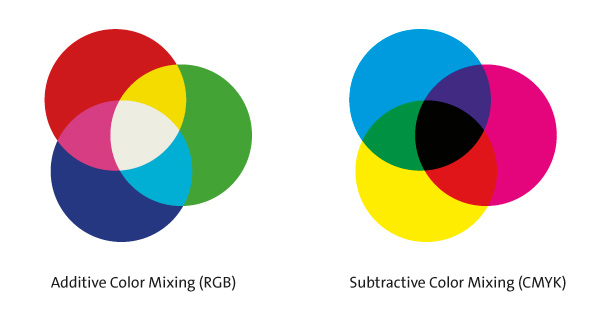
Today, art theorists widely agree that the concept of primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More is useful for categorization and orientation, but that the choice of primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More is quite arbitrary. Unlike Goethe and other artists believed, there is no such thing as pure primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More since it would be possible to choose any three colors to mix a gamut of the spectrum. While some primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More can mix a broad range of colors, it is impossible to mix the entire color spectrum based on a subtractive color mixing theory method.[28]
Primary ColorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More Depend on Device Type
The current theory is strongly influenced by the devices we use today. Desktop printers and other pigment color theory-based printing mechanisms with subtractive color mixing use an industry standard based on the CMYK color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More model with the colors cyan, magenta, yellow, and key/black. Color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More has it that with this specific set of colors, a broad range of colors can be mixed in inkInk, a liquid or paste used for writing, drawing, and printing, has played a crucial role in communication and artistic expression throughout history. Made from various pigments and dyes, ink allows for the transfer of text and images onto surfaces such as paper, fabric, and other materials. Types of Ink There are several types of ink, each serving different purposes More. However, the three colors cyan, magenta, and yellow are not able to mix black, which is why printers will have a separate cartridge for black color.
Computer screens and other light-based display devices with additive color mixing use an industry standard based on the RGB color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More for primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More, which are red, green, and blue. Almost all digital design tools will allow the user to define colors based on combining these three primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More, while the exact amount of each color per pixel is decided both by the computer’s graphics card and the quality of the monitor.

Human Experience of Color
Not only do most scientists today agree on the nature of color today, but there is also rapport for the experience of color being a highly subjective and complex phenomenon. Unlike Goethe and Itten’s color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, scientists today are convinced that it is impossible to create a universal color harmony theory. Instead, a number of factors will determine how an individual will respond to a specific color combination, such as age, gender, personal background, mood, as well as societal factors.[29]
Final Thoughts
With the knowledge about the history of color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More and being aware of the fact that there is no such thing as the correct primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More, artists and designers should be free to trust more their own eyes and to be open for experimentation. You will get the best results using an experimental approach to what complementary colours are working for you, what a respective theory means for you, and how you want to apply a color wheel theory.
Resources: Free Downloadables
Click here for the downloadable color theory quiz PDF.
Click here for the downloadable fun color theory quiz for kids PDF.
Download a free Colour Theory pdf
And check out the ultimate color palette generator.
Recommended Readings: Best Books about Color TheoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More and Famous Color Theorists
Color by Betty Edwards: A Course in Mastering the Art of Mixing Colors
The Secret Lives of Color by Cassia St Clair
Color Third Edition: A workshop for artists and designers
A Dictionary Of Color Combinations (English and Japanese Edition)
The Complete Color Harmony, Pantone Edition: Expert Color Information for Professional Results
You might also enjoy reading the following posts by Pigment Pool:
Gustav Klimt Inspired Art: Golden Influence on Modern Media and Pop Culture
Understanding Chinese Art: Colors and Their Cultural Significance
600 Art and Drawing Ideas to Ignite Your Imagination
Top 10 Tips on Applying Color Theory for Clothes
The Best Acrylic Paint Set for Artists and Hobbyists In 2022
A brief history of colour pigments
Mastering Art with Color Theory: Kandinsky’s Transformative Vision
The Psychology of Colour in Art: Masterpieces and Mind Games
Joan Miró Art Projects for Kids and Adults: Creative Fun for All Ages
Bamboo Art: Picture Serenity through Chinese Brushwork
[1] Azeemi, Samina T., and Mohsin Mohsin Raza. “A Critical Analysis of Chromotherapy and Its Scientific Evolution.” Advances in Pediatrics., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2 Dec. 2005, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1297510/.
[2] Loeb, James, and Jeffrey Henderson. “AristotleAristotle (384–322 BCE) was an ancient Greek philosopher and polymath whose extensive work has influenced numerous fields, including science, philosophy, and art. His contributions to color theory, although not as widely known, were groundbreaking for his era. Aristotle's observations and theories laid the groundwork for future studies in color and vision. Aristotle was a student of Plato and the teacher More, On Colours.” Loeb Classical Library, Harvard University Press, 26 Mar. 2018, www.loebclassics.com/view/aristotle- colours/1936/pb_LCL307.5.xml.
[3] Mahnke, Frank H., and Rudolf H. Mahnke. Color and Light in Man-made Environments. N.p.: Academy, 1999. Print.
[4] Loeb, James, and Jeffrey Henderson. “AristotleAristotle (384–322 BCE) was an ancient Greek philosopher and polymath whose extensive work has influenced numerous fields, including science, philosophy, and art. His contributions to color theory, although not as widely known, were groundbreaking for his era. Aristotle's observations and theories laid the groundwork for future studies in color and vision. Aristotle was a student of Plato and the teacher More, On Colours.” Loeb Classical Library, Harvard University Press, 26 Mar. 2018, www.loebclassics.com/view/aristotle- colours/1936/pb_LCL307.5.xml.
[5] O’Connor, J, and E. Robertson. “Abu Ali Al-Hasan Ibn Al-Haytham.” Yau Biography, School of Mathematics and Statistics University of St Andrews, Scotland , Nov. 1999, www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Al-Haytham.html.
[6] O’Connor 1999
[7] O’Connor 1999
[8] Jaeger, W. “Principles of Order in the Color Systems of the 17th Century. .” Advances in Pediatrics., U.S. National Library of Medicine, Apr. 1984, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6374264.
[9] Johnson, A. “COLOR THEORYColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More.” Color, MIT Optical Psychics , web.mit.edu/22.51/www/Extras/color_theory/color.html.
[10] Popova, Maria. “19th-Century Insight into the Psychology of Color and Emotion.” The Atlantic. Atlantic Media Company, 17 Aug. 2012. Web.
[11] Ball, Philip (2003) Bright Earth: Art and the Invention of Color, p. 25. University of Chicago Press
[12] Popova 2012
[13] Popova 2012
[14] Goethe, Johann Wolfgang von, and Charles Lock Eastlake. Goethe’s Theory of Colours. The Echo Library, 2016.
[15] Jaeger, W. “Principles of Order in the Color Systems of the 17th Century. .” Advances in Pediatrics., U.S. National Library of Medicine, Apr. 1984, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6374264.
[16] Popova 2012
[17] Lowengard, Sarah (2006) The Creation of Color in Eighteenth-Century Europe New York, para. 129-139, Columbia University Press)
[18] Ball 2003
[19] Popova 2012
[20] Popova 2012
[21] Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. “Thomas YoungThomas Young (1773–1829 CE) was an English polymath whose work spanned various fields, including physics, medicine, and Egyptology. His contributions to the study of light and color were particularly influential, laying the groundwork for modern wave theory and color vision. Born in Milverton, England, Young showed prodigious talents from a young age. He pursued studies in medicine but also made More.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 9 June 2018, www.britannica.com/biography/Thomas-Young.
[22] Johnson
[23] Piezo, Alegra. “Sir Isaac Newton’s Influence on the Color Wheel.” Munsell Color System; Color Matching from Munsell Color Company, 23 Jan. 2013, munsell.com/color- blog/sir-isaac-newton-color-wheel/.
[24] David Burton (1984), “Applying Color”, Art Education, USA: National Art Education Association, 37 (1): 40–43, doi:10.2307/3192794, JSTOR 3192794
[25] Itten, Johannes (1970) The Elements of Color. Van Nostrand Reinhold
[26] David Burton (1984), “Applying Color”, Art Education, USA: National Art Education Association, 37 (1): 40–43, doi:10.2307/3192794, JSTOR 3192794
[27] Albers, Josef (1963). Interaction of Color. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0300018462.
[28] MacEvoy, Bruce. Color Vision Handprint: Colormaking Attributes. N.p., 1 Aug. 2015. Web. 11 Jan. 2017.
[29] O’Connor, Zena (2010) Color Harmony Revisited, p. 267-273. Color Research and Application. Volume 35, Issue
FAQ: Quick Answers
Q: What is the history of color and its significance in art and science?
A: The history of color traces back to ancient civilizations, where colour theorists began exploring the emotional and psychological effects of colors, laying the groundwork for modern color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More in art and science.
Q : Who are some notable color theorists who have shaped our understanding of colors?
A: Notable color theorists include Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More, who first conceptualized the color wheel, and Johann Wolfgang von GoetheJohann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749–1832 CE) was a German writer, poet, scientist, and philosopher. He is best known for his literary works, but his contributions to the study of color were also groundbreaking and influential. Goethe's approach to color theory differed from the scientific perspective of his time, offering a more human-centered understanding of how we perceive color. His work, More, whose work on the theory of the color influenced both art and psychology.
Q: When was color first invented, and how has our perception of color evolved?
A: The concept of color as we understand it wasn’t “invented” but has been part of human perception since the beginning. The history of colours shows how our understanding and categorization have evolved, especially with the development of the color wheel by Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More.
Q: How did the color wheel come into existence, and who was behind its creation?
A: The color wheel was invented by Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More in the late 17th century. His experiments with prisms and light led to the understanding of color as a spectrum, revolutionizing the theories of colour.
Q: What role does color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More play in the field of art, and how has it influenced artistic expression?
A: Color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More plays a crucial role in art by guiding artists in their use of color to evoke emotions and convey messages. The history of colour in art shows how theories have shaped practices and styles, from Renaissance to modern digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More.
Q: Can you explain the colour definition in art and how it differs from general perceptions of color?
A: The colour definition in art involves not just the hueIn color theory, hue is one of the main properties of a color, defining its dominant wavelength. This characteristic determines whether we perceive a color as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or violet. Understanding hue is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color. Defining Hue • Definition: Hue is the degree to which a color can be described More but also the valueIn color theory, value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. This concept is crucial for artists and designers because it helps create depth, contrast, and visual interest in their work. Value is one of the three properties of color, alongside hue and saturation. Defining Value Value indicates how light or dark a color appears. It ranges from More and intensityIn color theory, intensity, also known as saturation or chroma, refers to the purity and vividness of a color. This property is essential for artists and designers as it helps create dynamic and engaging visuals. Intensity determines how bright or dull a color appears, influencing the overall impact and mood of a composition. Defining Intensity Intensity measures the degree of More of color as it relates to composition and expression. This definition is more nuanced than general perceptions, focusing on the emotional and symbolic uses of color.
Q: What is the significance of colour in history, and how has it impacted cultural and societal developments?
A: Colour in history has profound significance, symbolizing power, status, and emotions in various cultures. The history of colour reflects its impact on fashion, art, and symbolismSymbolism was a late 19th-century art movement of French, Belgian, and Russian origin. Poets and fine artists were seeking to represent absolute truths using metaphorical images in reaction against realism and naturalism. Content of both images and poetry were suggestive contents to express mystical ideas, emotions, and states of mind. Paul Gauguin, Nave Nave Mahana (1869) The term was coined More, influencing societal trends and cultural developments.
Q: How have theories of colour evolved from ancient times to the present day?
A: Theories of colour have evolved significantly, from Aristotle’s early speculations on color being a direct result of light and darkness to modern understandings of color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More and its application in design and marketing. This evolution reflects a deepening knowledge of how colors interact and affect us.
Q: What impact does the history of colors have on contemporary design and psychology?
A: The history of colors informs contemporary design and psychology by providing a rich context for the emotional and cognitive effects of color. Designers and psychologists draw on historical theories and applications to create environments and products that resonate on a psychological level.
Q: Who were the pioneers in the history of colour theory, and what were their contributions?
A: Pioneers in the history of colour theory include Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More, who introduced the idea of the spectrum of colors, and Albert Munsell, who developed a color classification system. Their contributions laid the foundation for understanding color relationships and the visual effects of color combinations.
Q: How does the colour of history influence our understanding of past events and cultures?
A: The colour of history influences our understanding by adding a layer of interpretation to historical events and cultures. Colors used in art, clothing, and symbols can reveal insights into societal values, beliefs, and emotional states of the past, offering a vivid window into how people lived and thought.
Q: In what ways have colour theorists contributed to our current understanding of visual aesthetics?
A: Colour theorists have contributed by developing frameworks and principles that explain how colors interact, influence mood, and affect perception. Their work has been instrumental in fields ranging from art and design to marketing and environmental design, shaping our current understanding of visual aesthetics.
Q: What are the key milestones in the history of colour, and how have they influenced modern color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More?
A: Key milestones include Newton’s prism experiments leading to the color spectrum, Goethe’s color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More, and the BauhausThe Bauhaus movement originated as a German school of the arts in the early 20th century. Founded by German architect Walter Gropius in 1919, the school was dedicated to uniting all branches of the arts under one roof. The Bauhaus acted as a hub for Europe's most experimental creatives, with well-known artist instructors like Wassily Kandinsky, Josef Albers, and Paul More school’s application of color in art and architecture. These milestones have profoundly influenced modern color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, integrating scientific, psychological, and aesthetic perspectives.
This article may contain compensated links. Please read Disclaimer for more info. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
