Albert Henry Munsell (1858–1918 CE) was an American painter, teacher, and the creator of the Munsell color system. His contributions to color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More and color science revolutionized the way colors are measured, categorized, and communicated, making a lasting impact on various industries, from art and design to manufacturing.
Born in Boston, Massachusetts, Munsell trained as an artist at the Massachusetts Normal Art School (now Massachusetts College of Art and Design) and later studied in Europe. His passion for color and its precise description led him to develop a systematic approach to color notation.

- Key Contributions:
- Developed the Munsell color system
- Authored “A Color Notation” and “Atlas of the Munsell Color System”
- Pioneered a scientific approach to color measurement
Munsell Color System: Munsell’s most notable achievement is the Munsell color system, which organizes colors based on three dimensions: hueIn color theory, hue is one of the main properties of a color, defining its dominant wavelength. This characteristic determines whether we perceive a color as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or violet. Understanding hue is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color. Defining Hue • Definition: Hue is the degree to which a color can be described More, valueIn color theory, value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. This concept is crucial for artists and designers because it helps create depth, contrast, and visual interest in their work. Value is one of the three properties of color, alongside hue and saturation. Defining Value Value indicates how light or dark a color appears. It ranges from More (lightness), and chroma (saturation). This system allows for precise and consistent communication of color.
- Color Dimensions:
- HueIn color theory, hue is one of the main properties of a color, defining its dominant wavelength. This characteristic determines whether we perceive a color as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or violet. Understanding hue is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color. Defining Hue • Definition: Hue is the degree to which a color can be described More: The type of color (e.g., red, green, blue)
- ValueIn color theory, value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. This concept is crucial for artists and designers because it helps create depth, contrast, and visual interest in their work. Value is one of the three properties of color, alongside hue and saturation. Defining Value Value indicates how light or dark a color appears. It ranges from More: The lightness or darkness of a color
- Chroma: The intensityIn color theory, intensity, also known as saturation or chroma, refers to the purity and vividness of a color. This property is essential for artists and designers as it helps create dynamic and engaging visuals. Intensity determines how bright or dull a color appears, influencing the overall impact and mood of a composition. Defining Intensity Intensity measures the degree of More or purity of a color
The Munsell color system arranges these dimensions in a three-dimensional space, providing a clear and objective way to describe colors.
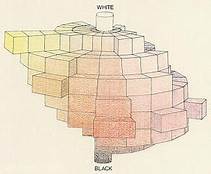
Color Notation: In his book “A Color Notation” (1905), Munsell introduced his color system to the public. He described how to identify and communicate color using his standardized notation, which became a crucial tool for artists, designers, and scientists.
- Standardized Notation:
- Provided a method to identify colors precisely
- Allowed for consistent color communication across different fields
- Facilitated the teaching and application of color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More
Munsell’s notation system was a breakthrough in achieving a universal language for color.
Atlas of the Munsell Color System: In 1915, Munsell published the “Atlas of the Munsell Color System,” which included color samples arranged according to his system. This atlas served as a practical reference for professionals working with color.
- Practical Reference:
- Included physical color samples arranged by hueIn color theory, hue is one of the main properties of a color, defining its dominant wavelength. This characteristic determines whether we perceive a color as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or violet. Understanding hue is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color. Defining Hue • Definition: Hue is the degree to which a color can be described More, valueIn color theory, value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. This concept is crucial for artists and designers because it helps create depth, contrast, and visual interest in their work. Value is one of the three properties of color, alongside hue and saturation. Defining Value Value indicates how light or dark a color appears. It ranges from More, and chroma
- Used as a standard reference in industries requiring precise color matching
- Helped establish consistent color standards in manufacturing and design
The atlas made the abstract concepts of the Munsell system tangible and usable in real-world applications.
Teaching and Influence: Munsell was a dedicated teacher, emphasizing the importance of color education. He taught at the Massachusetts Normal Art School, where he integrated his color system into the curriculum, influencing generations of artists and designers.
- Educational Impact:
- Promoted the importance of systematic color education
- Integrated scientific principles into art and design teaching
- Influenced future curricula and standards in color education
His efforts ensured that his scientific approach to color was widely adopted in art and design education.
Scientific Method: Munsell’s approach to color was highly empirical. He conducted experiments and gathered data to develop his system, ensuring that it was grounded in scientific observation and could be consistently applied.
- Methodology:
- Conducted rigorous experiments on color perception
- Gathered empirical data to inform his system
- Emphasized reproducibility and accuracy in color measurement
His scientific methodology set a standard for future research in color science.
Influence and Legacy: Munsell’s work had a profound impact on various fields. His color system is still widely used today in art, design, manufacturing, and even soil science, demonstrating its versatility and enduring relevance.
- Impact:
- Standardized color communication across multiple industries
- Influenced modern colorimetry and color science
- Left a legacy of integrating art and science in the study of color
Albert Henry Munsell’s pioneering work in color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More and his development of a systematic approach to color measurement continue to be invaluable resources for professionals and educators alike.
