- 1 The Basics of Color Theory
- 2 The Psychological Impact of Colors
- 3 Historical and Cultural Perspectives on Color
- 4 Famous Artists and Their Use of Color
- 5 Modern Applications of Color Psychology
- Practical Tips for Artists
- Transform Your Art with Color Psychology
- Additional Resources
- References
- Quick Facts and FAQ
Have you ever noticed how a room painted in blue makes you feel calm, while a red one might spark energy?
Colors shape our emotions and perceptions in subtle yet powerful ways.
Artists have harnessed the power of color for centuries, using it to convey and evoke feelings. While our moods may not change the color we see, the colors we encounter can significantly influence our mood and thoughts.
Today, we’ll dive into the psychology of colour in art. Let’s explore its history, cultural variations, and how artists use color to create emotional impact.
1 The Basics of Color Theory
Historical Background
Color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More has roots in the works of key historical figures. In the 15th century, Leon Battista Alberti, an Italian artist, and author, stressed the importance of color in art. His book “De Pictura” highlighted how mixing colors can create harmonious and realistic artworks.
Leonardo da Vinci built on Alberti’s ideas. He explored how light and shadow affect color and proposed a hierarchy of colors. His observations on color harmony and contrast influenced many artists.
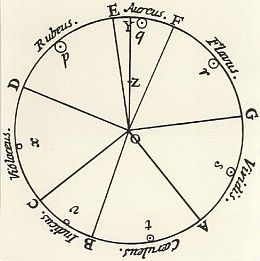
The most transformative contribution came from Isaac NewtonIsaac Newton (1642–1727 CE) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author who is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and significantly advanced the understanding of light and color. Born in Woolsthorpe, England, Newton made substantial contributions across various fields, but his work in optics and More in the 18th century. Newton’s experiments with prisms showed that white light splits into a spectrum of colors. His book “Opticks,” published in 1704, introduced the color wheel.
Isaac Newton’s Color Wheel
Newton’s color wheel arranges the spectrum in a circle, showing how colors transition smoothly from one to another. This visualization helps you understand how colors relate to each other. The wheel also highlights complementary colors, which are opposite each other and create striking contrasts.
Newton’s color wheel helps artists and designers understand color harmony, contrast, and the emotional impact of colors.
Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Colors
The color wheel is divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary colorsTertiary colors are the next step in the color mixing hierarchy, created by combining a primary color with a secondary color. These colors add depth and complexity to the color wheel, offering a rich array of hues for artists and designers. Understanding tertiary colors is essential for anyone looking to refine their color theory knowledge and apply it to their More. Primary colors—red, blue, and yellow—are the foundation. You can’t mix other colors to create them.
Secondary colorsSecondary colors are a fundamental aspect of color theory, created by mixing two primary colors in equal measure. The three secondary colors are green, orange, and purple. These colors expand the palette available to artists and designers, allowing for a broader range of hues and shades in their work. Understanding secondary colors is essential for anyone looking to deepen their More come from mixing two primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More: red and blue make purple, blue and yellow make green, and yellow and red make orange. These add more variety to your palette.
Tertiary colorsTertiary colors are the next step in the color mixing hierarchy, created by combining a primary color with a secondary color. These colors add depth and complexity to the color wheel, offering a rich array of hues for artists and designers. Understanding tertiary colors is essential for anyone looking to refine their color theory knowledge and apply it to their More are created by mixing a primary color with a secondary color next to it on the wheel. This gives you hues like red-orange, yellow-green, and blue-violet, offering more options for nuanced color schemes.
Understanding primary, secondary, and tertiary colorsTertiary colors are the next step in the color mixing hierarchy, created by combining a primary color with a secondary color. These colors add depth and complexity to the color wheel, offering a rich array of hues for artists and designers. Understanding tertiary colors is essential for anyone looking to refine their color theory knowledge and apply it to their More helps create balanced and dynamic artwork. The color wheel guides you in choosing colors that work well together and evoke the desired emotions.

2 The Psychological Impact of Colors
Overview of Color PsychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More
Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More studies how colors affect human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. Artists and marketers use this knowledge to evoke specific responses. Different colors can influence your mood, actions, and even physiological reactions. Understanding color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More helps you make more informed choices in art and design.

Red
Red is a color of passion and love, often used to grab attention. It can also signify aggression and anger, making it a powerful and sometimes overwhelming choice. In art, red can create a sense of urgency or highlight important elements. Marketers use red to stimulate appetite and attract attention to products.

Blue
Blue is calming and often associated with trust and authority. It’s a color that can lower blood pressure and create a sense of peace. Different cultures see blue differently; in some places, it symbolizes immortality or protection. In art and design, blue is used to evoke serenity and stability.

Yellow
Yellow is a cheerful color that can evoke feelings of happiness and energy. However, when used excessively, it can also cause frustration and anxiety. In marketing, yellow grabs attention and stimulates appetite, which is why many food brands use it. Artists use yellow to create warmth and highlight focal points.

Green
Green is closely linked to nature, symbolizing tranquility and health. It’s a refreshing color that can reduce stress and promote relaxation. Historically, green represented fertility and growth. Modern uses include eco-friendly branding and creating calming environments in design and art.

Purple
Purple signifies luxury, creativity, and imagination. Historically, it was a rare and expensive color, often associated with royalty and wealth. Today, purple is used in creative industries to inspire and captivate. In art, it can add a touch of elegance and depth.

Orange
Orange is an energetic and lively color that conveys enthusiasm and warmth. It’s highly visible and often used in marketing to attract attention and encourage action. In art, orange can evoke excitement and draw the viewer’s eye. Its cheerful nature makes it popular in both design and branding.

Black
Black represents power, elegance, and mystery. It’s a color of contrasts, often signifying sophistication as well as death and mourning. In Western cultures, black is chic and authoritative, commonly seen in fashion and formal wear. However, in some cultures, it’s associated with grief and loss. Artists use black to create depth and focus, enhancing the emotional impact of their work.

White
White symbolizes purity, innocence, and cleanliness in Western cultures. In contrast, it’s often associated with death and mourning in Eastern cultures. White can create a sense of space and simplicity in design. Artists use white to highlight and balance compositions.
3 Historical and Cultural Perspectives on Color
Throughout history, color has played a vital role in different cultures, symbolizing everything from power to spirituality. Ancient Egyptians used color for symbolic and therapeutic purposes, associating hues with gods and the afterlife. For example, green symbolized rebirth and fertility, while blue represented divinity and protection. In ancient China, color was crucial in feng shuiFeng Shui, an ancient Chinese practice, focuses on harmonizing individuals with their surrounding environment. Rooted in Taoist philosophy, it emphasizes the flow of energy (qi) and its impact on health, wealth, and overall well-being. Origins and History Feng Shui dates back thousands of years and has evolved through various Chinese dynasties. Initially used in the placement of tombs and homes, More, with each color linked to elements and energies to create balance and harmony in living spaces.

Cultural interpretations of color vary widely across societies. Red, seen as a color of passion and excitement in the West, is considered lucky and auspicious in China, often used in festivals and weddings. Yellow, associated with warmth and happiness in the West, holds imperial meaning in China, representing power and prosperity. Green, connected to nature and tranquility in many cultures, can also signify youth and fertility. Understanding these perspectives helps in using color thoughtfully and respectfully in a global context.
4 Famous Artists and Their Use of Color
Pablo Picasso
Pablo Picasso‘s use of color evolved dramatically throughout his career, with two notable periods being the Blue Period and the Rose Period. During his Blue Period (1901-1904), Picasso used shadesIn color theory, a shade is a darker version of a color, created by adding black to the original hue. This concept is essential for artists and designers, as it allows for a range of deeper, more intense tones that can add depth and drama to a composition. Defining Shade A shade results from mixing a pure hue with black. More of blue to convey feelings of sadness, loneliness, and despair. This phase began after the suicide of his close friend, Carlos Casagemas. A prime example is “The Old Guitarist” (1903), where the somber blue tonesIn color theory, a tone is a version of a color created by adding gray (a mix of black and white) to the original hue. This concept is essential for artists and designers as it allows for a wide range of colors that are neither too dark nor too light, providing versatility in creating depth, mood, and harmony within a More emphasize the subject’s isolation and melancholy.

In contrast, Picasso’s Rose Period (1904-1906) marked a shift to warmer tonesIn color theory, a tone is a version of a color created by adding gray (a mix of black and white) to the original hue. This concept is essential for artists and designers as it allows for a wide range of colors that are neither too dark nor too light, providing versatility in creating depth, mood, and harmony within a More such as pinks, reds, and earthy browns. These colors reflected a more optimistic and romantic outlook, likely influenced by his new relationship with Fernande Olivier. Works like “Family of Saltimbanques” (1905) showcase this change, using rosy hues to bring a sense of warmth and tenderness to the subjects.

Picasso’s strategic use of color in these periods demonstrates how he translated his emotional states into visual art, allowing viewers to feel the underlying sentiments through his palette choices. The stark difference between the cold blues and the warm pinks highlights his ability to manipulate color to evoke specific emotional responses.
Vincent van Gogh
Vincent van Gogh’s use of color was both vibrant and expressive, reflecting his intense emotions and inner turmoil. Art historians have understood his use of yellows and blues to convey his feelings and states of mind, creating some of his most iconic works.
Van Gogh’s “Starry Night” (1889) is a prime example of his use of blue to depict his turbulent state. The swirling blues of the night sky are often interpreted as conveying a sense of movement and chaos, reflecting his mental struggles during his time at the Saint-Paul-de-Mausole asylum. The contrast between the calm village and the tumultuous sky emphasizes this inner conflict.

In contrast, van Gogh’s use of yellow is often seen as conveying a sense of hope and warmth, yet it also carries a manic intensityIn color theory, intensity, also known as saturation or chroma, refers to the purity and vividness of a color. This property is essential for artists and designers as it helps create dynamic and engaging visuals. Intensity determines how bright or dull a color appears, influencing the overall impact and mood of a composition. Defining Intensity Intensity measures the degree of More. Art historians suggest that “Sunflowers” (1888), a series where he used various shadesIn color theory, a shade is a darker version of a color, created by adding black to the original hue. This concept is essential for artists and designers, as it allows for a range of deeper, more intense tones that can add depth and drama to a composition. Defining Shade A shade results from mixing a pure hue with black. More of yellow, expresses his admiration for nature’s beauty and his desire for happiness. However, the intensityIn color theory, intensity, also known as saturation or chroma, refers to the purity and vividness of a color. This property is essential for artists and designers as it helps create dynamic and engaging visuals. Intensity determines how bright or dull a color appears, influencing the overall impact and mood of a composition. Defining Intensity Intensity measures the degree of More of the yellows may also suggest a kind of desperation and urgency.
Another notable example is “The Yellow House” (1888), where van Gogh painted his home in Arles. The vibrant yellows and blues in the paintingPainting is a fundamental form of visual art that has been practiced for thousands of years. It involves applying pigment to a surface such as canvas, paper, or a wall. Painting can be explored through various styles, techniques, and mediums, each offering unique possibilities for expression and creativity. Historical Background • Ancient Beginnings: The history of painting dates back to More are interpreted as conveying his optimism and his dream of creating an artist community, which was a brief period of hope in his troubled life.

Through his use of these colors, van Gogh not only depicted the world around him but also provided a window into his emotional and psychological state. His bold and expressive color choices continue to resonate deeply with viewers, making his works timeless expressions of human emotion.
Claude Monet
Claude Monet’s use of color, especially green, played a vital role in his portrayals of nature. Art historians often highlight how he used green to convey the lush, tranquil qualities of the natural world.
In “Water Lilies” (1916), Monet’s extensive use of greens creates a serene and immersive landscape. The various shadesIn color theory, a shade is a darker version of a color, created by adding black to the original hue. This concept is essential for artists and designers, as it allows for a range of deeper, more intense tones that can add depth and drama to a composition. Defining Shade A shade results from mixing a pure hue with black. More of green in the water and foliage emphasize the lushness and tranquility of his garden at Giverny. This paintingPainting is a fundamental form of visual art that has been practiced for thousands of years. It involves applying pigment to a surface such as canvas, paper, or a wall. Painting can be explored through various styles, techniques, and mediums, each offering unique possibilities for expression and creativity. Historical Background • Ancient Beginnings: The history of painting dates back to More series is noted for its ability to transport viewers into a peaceful, natural setting.

Monet also used other colors to capture the changing effects of light and seasons. In “Impression, Sunrise” (1872), he used blues and oranges to paint the sunrise over the harbor of Le Havre. The interplay of these colors captures the fleeting moment of dawn, showcasing his fascination with light and its impact on the landscape.

“Haystacks” (1890-1891) is another example where Monet explored color to show different times of the day and seasons. By using purples, pinks, and golds, Monet was able to show how the same subject could transform under varying lighting conditions.

Monet’s mastery of color portrayed nature accurately and conveyed its emotional and sensory impact at the same time. His use of green and other vibrant colors continues to be celebrated for capturing the essence and beauty of the natural world.
Georgia O’Keeffe
When you look at Georgia O’Keeffe’s floral paintings, you’ll notice her stunning use of purple. Art historians note how she used this color to evoke both beauty and depth.
In “Purple Petunias” (1925), O’Keeffe’s bold use of purple draws you in, making the flowers appear almost larger than life. The rich, vibrant purples highlight the delicate yet powerful nature of the petals, inviting you to appreciate their intricate details.

O’Keeffe’s “Jimson Weed” (1936) also showcases her mastery of color. The subtle purples in the shadows of the white flowers add dimension and complexity, transforming a simple bloom into a captivating subject.

By using purple, O’Keeffe not only captured the physical beauty of flowers but also conveyed their emotional impact. Her work invites you to see the natural world with fresh eyes, appreciating the vivid hues that bring her subjects to life.
Edvard Munch
When you explore Edvard Munch’s work, you can see how he used bold colors to express deep psychological themes. His paintingPainting is a fundamental form of visual art that has been practiced for thousands of years. It involves applying pigment to a surface such as canvas, paper, or a wall. Painting can be explored through various styles, techniques, and mediums, each offering unique possibilities for expression and creativity. Historical Background • Ancient Beginnings: The history of painting dates back to More “The Scream” (1893) is a powerful example.

In “The Scream,” Munch’s use of intense reds and oranges in the sky creates a sense of panic and chaos. These vibrant colors contrast sharply with the dark blues and blacks of the swirling background, enhancing the feeling of despair and anxiety.
The figure at the center, painted in ghostly white, stands out against the vivid backdrop. This stark contrast amplifies the sense of isolation and fear, drawingDrawing is a foundational art form that involves creating images on a surface, typically paper, using tools such as pencils, pens, and charcoal. It is a versatile medium that allows artists to express ideas, emotions, and stories through lines, shapes, and shading. Historical Background • Prehistoric Beginnings: The earliest known drawings date back to prehistoric times, with cave drawings found More you into the emotional turmoil depicted.
Munch’s use of bold colors in this and other works was a way to visually express complex emotions. His approach allows you to feel the psychological intensityIn color theory, intensity, also known as saturation or chroma, refers to the purity and vividness of a color. This property is essential for artists and designers as it helps create dynamic and engaging visuals. Intensity determines how bright or dull a color appears, influencing the overall impact and mood of a composition. Defining Intensity Intensity measures the degree of More he intended to convey, making his art deeply impactful.
Henri Matisse
Henri Matisse’s use of bold, primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More is a defining feature of his work. When you look at his paintings, the vibrant reds, blues, and yellows jump out, creating a sense of energy and emotion.
In “The Dance” (1910), Matisse uses bright reds and blues to capture the movement and joy of the dancers. The boldness of these primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More makes the scene feel alive and full of energy.

“The Red Studio” (1911) is another example where Matisse fills the canvas with intense red. This dominant color transforms the room into a dynamic space, highlighting the artist’s tools and works with a vibrant backdrop.

Matisse’s use of primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More isn’t just about visual impact. It’s about evoking feelings and creating a lively, emotional experience for you as the viewer. His approach makes his work instantly recognizable and deeply engaging.
Mark Rothko
Mark Rothko’s paintings are known for their large fields of color, designed to evoke deep emotional responses. When you stand before one of his works, the sheer size and intensityIn color theory, intensity, also known as saturation or chroma, refers to the purity and vividness of a color. This property is essential for artists and designers as it helps create dynamic and engaging visuals. Intensity determines how bright or dull a color appears, influencing the overall impact and mood of a composition. Defining Intensity Intensity measures the degree of More of the colors can be overwhelming.
In “No. 61 (Rust and Blue)” (1953), Rothko uses expansive blocks of rust and blue to create a meditative space. The colors seem to pulse and shift, drawingDrawing is a foundational art form that involves creating images on a surface, typically paper, using tools such as pencils, pens, and charcoal. It is a versatile medium that allows artists to express ideas, emotions, and stories through lines, shapes, and shading. Historical Background • Prehistoric Beginnings: The earliest known drawings date back to prehistoric times, with cave drawings found More you into a contemplative state.

“Orange, Red, Yellow” (1961) features vibrant, layered rectangles of color that seem to float and interact. The warm hues can stir feelings of warmth and intensityIn color theory, intensity, also known as saturation or chroma, refers to the purity and vividness of a color. This property is essential for artists and designers as it helps create dynamic and engaging visuals. Intensity determines how bright or dull a color appears, influencing the overall impact and mood of a composition. Defining Intensity Intensity measures the degree of More, inviting you to reflect on your emotions.

Rothko’s technique of layeringLayering is a fundamental technique in art that involves building up multiple layers of material to create depth, texture, and complexity in a composition. This approach is used in various art forms, including painting, drawing, digital art, and mixed media. Layering allows artists to add richness and dimension to their work, making it more dynamic and engaging. Defining Layering Layering More and blending these large color fields aims to create an immersive experience. His goal was to connect with you on a deeply emotional level, using color to transcend beyond the visual to the emotional.
Jackson Pollock
Jackson Pollock’s action paintings are renowned for their dynamic use of color, conveying both movement and emotion. When you observe his work, you can almost feel the energy and intensityIn color theory, intensity, also known as saturation or chroma, refers to the purity and vividness of a color. This property is essential for artists and designers as it helps create dynamic and engaging visuals. Intensity determines how bright or dull a color appears, influencing the overall impact and mood of a composition. Defining Intensity Intensity measures the degree of More he poured into each piece.
In “No. 5, 1948,” Pollock’s splashes of yellows, blacks, and reds create a chaotic yet harmonious composition. The colors seem to dance and collide, capturing a sense of raw, unfiltered emotion.

“Blue Poles” (1952) showcases his ability to use blues and oranges to create depth and rhythm. The intertwining colors and bold strokes guide your eyes across the canvas, making you feel the frenetic energy of his paintingPainting is a fundamental form of visual art that has been practiced for thousands of years. It involves applying pigment to a surface such as canvas, paper, or a wall. Painting can be explored through various styles, techniques, and mediums, each offering unique possibilities for expression and creativity. Historical Background • Ancient Beginnings: The history of painting dates back to More process.

Pollock’s technique of dripping and flinging paint allowed him to capture the essence of motion. His vibrant color choices and spontaneous application convey a visceral emotional impact, making his work both captivating and emotionally charged.
Wassily Kandinsky
Wassily Kandinsky’s abstract use of color was a groundbreaking approach to conveying spiritual and emotional content. When you view his paintings, the vibrant hues and dynamic compositions aim to evoke a deeper connection.
In “Composition VIII” (1923), Kandinsky uses a mix of bold and subtle colors to create a sense of harmony and balance. The interplay of shapes and colors is meant to resonate with your inner emotions, stimulating a spiritual response.

“Yellow-Red-Blue” (1925) features striking contrasts between its primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More, each hueIn color theory, hue is one of the main properties of a color, defining its dominant wavelength. This characteristic determines whether we perceive a color as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or violet. Understanding hue is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color. Defining Hue • Definition: Hue is the degree to which a color can be described More carrying its own emotional weight. The vibrant yellow suggests energy and optimism, while the deep blue invites contemplation and calm.

Kandinsky believed that color could directly affect the soul, much like music. His abstract compositions are designed to engage you on an emotional and spiritual level, using color as a powerful tool for inner connection and emotional expression.
Joan Miró
Joan Miró‘s use of bright, primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More is a hallmark of his work, evoking rich subconscious imagery. When you look at his paintings, the vibrant reds, blues, and yellows immediately capture your attention and stimulate the imagination.
In “The Farm” (1921-1922), Miró’s use of bright colors against a detailed backdrop brings everyday objects to life, creating a dreamlike quality. The vivid hues suggest a deeper, subconscious world where ordinary items take on symbolic meanings.

“Harlequin’s Carnival” (1924-1925) is another excellent example. The bold primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More animate a whimsical scene filled with fantastical creatures and abstract forms. These colors create a playful yet surreal atmosphere, inviting you to explore the hidden layers of the mind.

Miró’s technique often involves using simple shapes and primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More to create complex, subconscious narratives. His vibrant palette and imaginative compositions draw you into a world where the line between reality and fantasy blurs, encouraging a deeper, intuitive engagement with his art.
Paul Klee
Paul Klee’s playful and experimental use of color is a defining feature of his work. When you explore his paintings, you’ll notice his unique ability to blend whimsy with depth.
In “Senecio” (1922), Klee uses warm, contrasting colors to create a face that feels both abstract and familiar. The playful use of reds, yellows, and oranges gives the piece a childlike charm while still provoking thought.

“Ad Parnassum” (1932) showcases Klee’s experimentation with color and form. The paintingPainting is a fundamental form of visual art that has been practiced for thousands of years. It involves applying pigment to a surface such as canvas, paper, or a wall. Painting can be explored through various styles, techniques, and mediums, each offering unique possibilities for expression and creativity. Historical Background • Ancient Beginnings: The history of painting dates back to More is filled with tiny, mosaic-like squares in a range of colors, creating a harmonious yet dynamic composition. This technique draws you into a complex visual experience.

Klee’s work often involves a blend of vibrant and muted colors to explore various themes and emotions. His playful approach invites you to see color in new ways, blending fantasy with reality and making each piece a delightful puzzle to decode.
Piet Mondrian
Piet Mondrian’s use of primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More and geometric shapes is central to his style, creating a sense of harmony and balance. When you look at his paintings, the simplicity and precision immediately stand out.
In “Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow” (1930), Mondrian uses red, blue, and yellow alongside black and white. The careful arrangement of squares and rectangles, combined with bold black lines, creates a balanced and harmonious composition.

“Broadway Boogie Woogie” (1942-1943) showcases Mondrian’s evolution in using primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More and geometric shapes. Inspired by the rhythm of New York City, the painting’s grid-like pattern and vibrant colors convey a lively yet ordered dynamic.

Mondrian’s method involves reducing elements to their basic forms and colors. This approach allows you to appreciate the pure visual harmony and balance he achieved, emphasizing how simplicity can lead to profound aesthetic experiences.
Andy Warhol
Andy Warhol’s use of bright, contrasting colors is a signature element of his pop artPop Art is a dynamic genre of modern art that emerged during the mid-20th century as a bold challenge to traditional art conventions. It focused on popular culture, using images from advertising, comic books, and the everyday to comment on the nature of mass production and consumerism. This entry delves into the key concepts, artists, and the broader impact of More. His bold color choices create striking visual contrasts that capture your attention and convey his themes effectively.
In “Marilyn Diptych” (1962), Warhol uses vibrant colors like hot pink, yellow, and blue to depict Marilyn Monroe. The contrasting hues highlight her iconic status while also commenting on the commodification of celebrity culture.

“Campbell’s Soup Cans” (1962) features repeated images of soup cans, each painted with bright, contrasting colors. This repetition and color contrast make a mundane object pop, turning it into a powerful commentary on consumerism and mass production.

Warhol’s technique of using silkscreen printing allowed him to apply these bold colors consistently. His work invites you to see familiar images in a new light, challenging traditional perceptions and celebrating popular culture with a vivid, dynamic palette.
Frida Kahlo
Frida Kahlo’s use of vivid colors is a powerful tool in expressing her personal pain and cultural identity. When you look at her paintings, the vibrant hues immediately convey deep emotions and rich cultural narratives.
In “The Two Fridas” (1939), Kahlo uses bold reds and greens to depict her dual heritage and emotional turmoil. The vivid blood-red heart and the stark white dress highlight her pain and vulnerability, contrasting sharply with the lush, green background that symbolizes life and growth.

“Self-Portrait with Thorn Necklace and Hummingbird” (1940) features bright yellows, blues, and greens. The vibrant colors contrast with the dark themes of pain and suffering, as depicted by the thorn necklace and the lifeless hummingbird. This juxtaposition emphasizes her resilience and connection to her Mexican roots.

Kahlo’s use of color is deeply tied to her identity. The rich, vibrant palette reflects the traditional Mexican folk artFolk art represents the creative expressions of ordinary people, often rooted in community traditions and cultural practices. It encompasses a wide range of artistic forms and styles, reflecting the everyday life, beliefs, and values of various cultures. Unlike fine art, folk art is typically created by self-taught artists, and its beauty lies in its simplicity and directness. Characteristics of Folk More that influenced her, while also serving as a medium to articulate her personal experiences. Her bold color choices invite you to feel her struggles and triumphs, making her work profoundly moving and evocative.
Gustav Klimt
Gustav Klimt’s use of gold and rich colors is a hallmark of his symbolic and decorative works. When you view his paintings, the luxurious hues and shimmering gold immediately draw you in, creating a sense of opulence and depth.
In “The Kiss” (1907-1908), Klimt uses gold leaf extensively, combined with vibrant yellows and deep reds. The gold adds a sense of timelessness and grandeur, while the rich colors emphasize the intimacy and passion between the figures.

“Adele Bloch-Bauer I” (1907) showcases Klimt’s mastery of combining gold with intricate patterns and rich colors. The golden background and ornate details highlight the subject’s elegance and status, while the deep blues and greens add depth and complexity.

Klimt’s use of gold and rich colors wasn’t just for aesthetic purposes. It was also symbolic, reflecting themes of love, beauty, and transcendence. His lavish color paletteA color palette refers to a selection of colors used in design and art. It can set the tone, convey emotions, and highlight key elements. color wheel Types of Color Palettes • Monochromatic: Uses variations in lightness and saturation of a single color. Ideal for creating a harmonious and cohesive look. • Analogous: Combines colors that are next to each More invites you to explore the layers of meaning in his work, blending beauty with profound symbolismSymbolism was a late 19th-century art movement of French, Belgian, and Russian origin. Poets and fine artists were seeking to represent absolute truths using metaphorical images in reaction against realism and naturalism. Content of both images and poetry were suggestive contents to express mystical ideas, emotions, and states of mind. Paul Gauguin, Nave Nave Mahana (1869) The term was coined More.
5 Modern Applications of Color Psychology
Marketing and Branding
Companies use color to influence consumer behavior and create strong brand identities. Whole Foods uses green in its branding to evoke freshness, health, and eco-friendliness. McDonald’s employs yellow and red, which are known to stimulate appetite and convey happiness and urgency, drawingDrawing is a foundational art form that involves creating images on a surface, typically paper, using tools such as pencils, pens, and charcoal. It is a versatile medium that allows artists to express ideas, emotions, and stories through lines, shapes, and shading. Historical Background • Prehistoric Beginnings: The earliest known drawings date back to prehistoric times, with cave drawings found More customers in quickly.


Interior Design
Colors in interior design are carefully chosen to evoke specific moods and feelings. Blues and greens create a calming, serene environment, ideal for bedrooms and bathrooms. Meanwhile, warm colors like red and orange can make a space feel energetic and lively, often used in living rooms and dining areas.

Digital Art and Media
In digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More, social media, and user interface design, color can be used to drive user engagement. Photo filters on apps like Instagram use warm tonesIn color theory, a tone is a version of a color created by adding gray (a mix of black and white) to the original hue. This concept is essential for artists and designers as it allows for a wide range of colors that are neither too dark nor too light, providing versatility in creating depth, mood, and harmony within a More to make images more inviting. A/B testing in marketing shows that different colors on call-to-action buttons can significantly impact user behavior and conversion rates, with colors like red and green often tested for their psychological effects.

Practical Tips for Artists
Choosing a Palette
Selecting the right color paletteA color palette refers to a selection of colors used in design and art. It can set the tone, convey emotions, and highlight key elements. color wheel Types of Color Palettes • Monochromatic: Uses variations in lightness and saturation of a single color. Ideal for creating a harmonious and cohesive look. • Analogous: Combines colors that are next to each More helps evoke specific emotions in your artwork. Start by considering the mood you want to convey:
- Warm Colors: Reds, oranges, and yellows can evoke feelings of warmth, excitement, and passion.
- Cool Colors: Blues, greens, and purples are often associated with calmness, tranquility, and sadness.

To create harmony, use colors that are adjacent on the color wheel, known as analogous colors. For contrast and to make elements stand out, choose complementary colors, which are opposite each other on the wheel.
Tips for Choosing Your Palette:
- Think about the emotional impact: Decide on the mood you want your piece to evoke.
- Use tools: Digital color pickers and swatches can help you visualize how colors will interact.
- Experiment with shadesIn color theory, a shade is a darker version of a color, created by adding black to the original hue. This concept is essential for artists and designers, as it allows for a range of deeper, more intense tones that can add depth and drama to a composition. Defining Shade A shade results from mixing a pure hue with black. More and tonesIn color theory, a tone is a version of a color created by adding gray (a mix of black and white) to the original hue. This concept is essential for artists and designers as it allows for a wide range of colors that are neither too dark nor too light, providing versatility in creating depth, mood, and harmony within a More: Try different variations of your chosen colors to find the perfect balance.

Remember, the context and cultural background of your audience can also influence how colors are perceived. By thoughtfully choosing your palette, you can enhance the emotional impact of your work and better connect with your audience.
Experimenting with Color
Experimenting with color combinations can help you discover what works best for your style and message. Don’t be afraid to mix and match colors to see how they interact.
Tips for Experimenting with Color:
- Start with a Base: Choose a few colors that you feel comfortable with as a foundation.

- Add Variety: Introduce new colors gradually and see how they change the mood of your work.
- Play with Contrast: Try pairing complementary colors to create striking contrasts or analogous colors for a more harmonious feel.

Use tools like paper color wheels or digital color wheels and swatches to test combinations before applying them to your artwork.

Benefits of Experimentation:
- Discover New Styles: You might find a unique color paletteA color palette refers to a selection of colors used in design and art. It can set the tone, convey emotions, and highlight key elements. color wheel Types of Color Palettes • Monochromatic: Uses variations in lightness and saturation of a single color. Ideal for creating a harmonious and cohesive look. • Analogous: Combines colors that are next to each More that sets your work apart.
- Enhance Your Message: Colors can emphasize aspects of your work, adding depth and meaning.
- Build Confidence: The more you experiment, the more confident you’ll become in your color choices.
Remember, color experimentation is about finding what resonates with you and your audience. It’s an ongoing process that evolves as you grow as an artist.
Color in Digital Art
Digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More offers unique opportunities compared to traditional media. Digital tools provide you with a vast array of colors and the ability to manipulate them with precision.
Differences from Traditional Media:
- Unlimited Palette: Unlike traditional media, digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More offers an unlimited color paletteA color palette refers to a selection of colors used in design and art. It can set the tone, convey emotions, and highlight key elements. color wheel Types of Color Palettes • Monochromatic: Uses variations in lightness and saturation of a single color. Ideal for creating a harmonious and cohesive look. • Analogous: Combines colors that are next to each More. You can create any hueIn color theory, hue is one of the main properties of a color, defining its dominant wavelength. This characteristic determines whether we perceive a color as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or violet. Understanding hue is essential for artists, designers, and anyone working with color. Defining Hue • Definition: Hue is the degree to which a color can be described More, shade, or gradient with a few clicks.
- Editability: Digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More allows for easy adjustments. You can experiment with different colors without worrying about ruining your work.
- Consistency: Digital tools ensure consistent color application, which can be difficult to achieve with traditional paints and materials.
Advantages of Digital Color:
- LayeringLayering is a fundamental technique in art that involves building up multiple layers of material to create depth, texture, and complexity in a composition. This approach is used in various art forms, including painting, drawing, digital art, and mixed media. Layering allows artists to add richness and dimension to their work, making it more dynamic and engaging. Defining Layering Layering More: Digital platforms let you work with layers, enabling complex color compositions and easy corrections.
- Special Effects: Digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More software offers tools for adding special effects, like glows and textures, that are hard to replicate traditionally.
- Speed: Changes and adjustments are faster, allowing for more experimentation and iteration.
Challenges in Digital Color:
- Screen Variability: Colors may look different on various screens, making it necessary to check your work on multiple devices.
- Color Depth: Digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More may lack the texture and depth of traditional media, requiring artists to use techniques like shading and gradients to add dimension.
Tips for Using Color in Digital ArtDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More:
- Calibrate Your Monitor: Ensure your colors are accurate across different devices.
- Use Color TheoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More: Apply traditional color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More principles to your digital work for balanced and harmonious results.
- Experiment with Tools: Take advantage of digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More tools and features to explore new color possibilities.
Digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More opens up endless possibilities for creative expression through color. By understanding its unique advantages and challenges, you can harness the full potential of digital color in your artwork.

Transform Your Art with Color Psychology
Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More in art shapes emotions, tells stories, and connects with viewers on a deep level.
From historical insights and psychological impacts of various colors to practical tips for using color effectively in both traditional and digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More, you are now well-equipped to dive right into your own color adventures.
I’ve always found that experimenting with different colors can transform a piece in unexpected ways. Try out the tips discussed and see how they influence your work. Let color guide your creative journey and inspire new possibilities in your art.

Additional Resources
Books and Articles:
- “Interaction of Color” by Josef AlbersJosef Albers (1888–1976) was a German-American artist, educator, and influential figure in the fields of color theory and abstract art. Known for his profound impact on modern art education, Albers' work emphasized the perception and interaction of color. Born in Bottrop, Germany, Albers initially trained as a schoolteacher before pursuing his passion for art. He studied at the Bauhaus, where More: A comprehensive book on color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More and its application in art.
- “Color PsychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More and Color Therapy” by Faber Birren: A detailed exploration of how colors affect emotions and behavior.
- “The Secret Lives of Color” by Kassia St. Clair: An engaging read about the history and significance of various colors.
- Color TheoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More in Art: The Color Wheel and Finding Complementary Colors by Draw Paint Academy: An online article explaining the basics of color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More.
Online Tools:
- Adobe Color: A versatile tool for creating and experimenting with color schemes.
- Coolors: An easy-to-use color scheme generator that helps you explore different palettes.
- Paletton: A color scheme designer that allows you to create harmonious color combinations.
- Color Hunt: A collection of beautiful color palettes curated by designers.

References
Whole Foods’ Branding: Whole Foods Market
McDonald’s Branding: McDonald’s
Interior Design and Color: Architectural Digest
Digital ArtDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More and Media: Creative Bloq
Elliot, A. J. (2015). Color and psychological functioning: A review of theoretical and empirical work. Frontiers in Psychology, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00368
Interaction Design Foundation. (n.d.). What is color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More? https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/color-theory
Pressbooks. (n.d.). Colour psychology and physiology. https://rmit.pressbooks.pub/colourtheory1/chapter/colour-psychology-physiology/
Van Edwards, V. (2022, March 22). Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More: How color affects your emotions and why. Science of People. https://www.scienceofpeople.com/color-psychology/
Stec, C. (2022, August 16). Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More in marketing and brand identity. HelpScout. https://www.helpscout.com/blog/psychology-of-color/
Cherry, K. (2022, November 21). Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More: Does it affect how you feel? Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/color-psychology-2795824
Cyr, D., Head, M., & Larios, H. (2010). Colour appeal in website design within and across cultures: A multi-method evaluation. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 68(1-2), 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2009.08.005
Schloss, K. B., & Palmer, S. E. (2011). Aesthetic response to color combinations: Preference, harmony, and similarity. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 73(2), 551-571. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-010-0027-0
Gao, X. P., Xin, J. H., Sato, T., Hansuebsai, A., Scalzo, M., Kajiwara, K., … & Billger, M. (2007). Analysis of cross-cultural color emotion. Color Research & Application, 32(3), 223-229. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.20321
Terwogt, M. M., & Hoeksma, J. B. (1995). Colors and emotions: Preferences and combinations. The Journal of General Psychology, 122(1), 5-17. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221309.1995.9921217
Valdez, P., & Mehrabian, A. (1994). Effects of color on emotions. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 123(4), 394-409. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.123.4.394
Hupka, R. B., Zaleski, Z., Otto, J., Reidl, L., & Tarabrina, N. V. (1997). The colors of anger, envy, fear, and jealousy: A cross-cultural study. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 28(2), 156-171. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022197282002
Boyatzis, C. J., & Varghese, R. (1994). Children’s emotional associations with colors. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 155(1), 77-85. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221325.1994.9914760
Manav, B. (2007). Color-emotion associations and color preferences: A case study for residences. Color Research & Application, 32(2), 144-150. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.20294
Kaya, N., & Epps, H. H. (2004). Relationship between color and emotion: A study of college students. College Student Journal, 38(3), 396-405.
Sliburyte, L., & Skeryte, I. (2014). What we know about consumers’ color perception. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 156, 468-472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.11.223
Sorokowski, P., Sorokowska, A., Frackowiak, T., Huk, A., & Pisanski, K. (2021). Color preferences across societies. Color Research & Application, 46(6), 1232-1241. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.22688
Birren, F. (2013). Color psychology and color therapy. Pickle Partners Publishing.
Eckstut, J., & Eckstut, A. (2013). The secret language of color. Black Dog & Leventhal Publishers.
Gage, J. (1999). Color and meaning: Art, science, and symbolism. University of California Press.
Gurney, J. (2010). Color and light: A guide for the realist painter. Andrews McMeel Publishing.
Hardin,C. (2011). Color for philosophers: Unweaving the rainbow. Oxford University Press.
Finlay, V. (2004). Color: A natural history of the palette. Ballantine Books.
Bradley, M. (2011). Color and meaning in ancient Rome. Cambridge University Press.
McLaury, R. (2017). Color and meaning in ancient Mesoamerica. Routledge.

Quick Facts and FAQ
Q: What is color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More in art?
A: Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More in art studies how colors affect human emotions, behavior, and perceptions. Artists use this understanding to evoke specific feelings and reactions through their color choices. By manipulating hues, they can create moods, emphasize certain elements, and convey deeper messages. Understanding color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More enhances the emotional impact of artworks.
Q: How do primary colorsPrimary colors form the foundation of color theory and are essential to understanding how colors work together. The primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. These colors are unique because they cannot be created by mixing other colors together. Instead, they are the source colors that mix to create a broad spectrum of hues used in art, design, and everyday More influence art?
A: Primary colors—red, blue, and yellow—are the foundation of all other colors. They cannot be created by mixing other colors and serve as the starting point for creating a wide range of hues. In art, they are used to create vibrant and striking compositions. Their simplicity and boldness make them powerful tools for artists.
Q: Why did Vincent van GoghVincent van Gogh (1853 – 1890) is one of the renowned Post-Impressionist artists, best known for his striking use of colour, emphatic brushwork, and contoured forms. As a son of a pastor, the Dutch artist war brought up in a religious and cultured atmosphere. After working unsuccessfully as a clerk at a bookstore, as a salesman, and as a preacher More use vibrant yellows and blues?
A: Art historians suggest that van Gogh used vibrant yellows to convey hope and warmth, while blues depicted his inner turmoil and emotional struggles. In works like “Starry Night” and “Sunflowers,” these colors create strong emotional contrasts. The intensityIn color theory, intensity, also known as saturation or chroma, refers to the purity and vividness of a color. This property is essential for artists and designers as it helps create dynamic and engaging visuals. Intensity determines how bright or dull a color appears, influencing the overall impact and mood of a composition. Defining Intensity Intensity measures the degree of More of his palette reflects his passionate and tumultuous state of mind. His color choices continue to evoke powerful emotional responses in viewers.
Q: How does digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More differ from traditional art in terms of color use?
A: Digital artDigital art refers to a range of artistic works and practices that use digital technology as an essential part of the creative or presentation process. Since the 1970s, various names have been used to describe the process, including computer art and multimedia art. Digital art is itself placed under the larger umbrella term of new media art. The digital art More offers an unlimited color paletteA color palette refers to a selection of colors used in design and art. It can set the tone, convey emotions, and highlight key elements. color wheel Types of Color Palettes • Monochromatic: Uses variations in lightness and saturation of a single color. Ideal for creating a harmonious and cohesive look. • Analogous: Combines colors that are next to each More and allows for easy adjustments, unlike traditional media. Artists can experiment with hues and shadesIn color theory, a shade is a darker version of a color, created by adding black to the original hue. This concept is essential for artists and designers, as it allows for a range of deeper, more intense tones that can add depth and drama to a composition. Defining Shade A shade results from mixing a pure hue with black. More without the fear of making irreversible mistakes. Digital tools provide consistent color application, enhancing precision. However, colors may vary across different screens, which can pose a challenge.
Q: How can interior design use color to create specific moods?
A: Interior designers use color to evoke specific moods and feelings within a space. Blues and greens create a calming and serene environment, ideal for bedrooms and bathrooms. Warm colors like red and orange can make a space feel energetic and lively, often used in living rooms and dining areas. Thoughtful color choices can transform the ambiance of any room.
Q: Why is experimenting with color important for artists?
A: Experimenting with color allows artists to discover new combinations that enhance their style and message. It helps them understand how different hues interact and the emotional responses they can evoke. This process can lead to unique and innovative artworks that stand out. Continual experimentation keeps an artist’s work dynamic and engaging.
Q: How do cultural variations affect color perception?
A: Different cultures assign various meanings and emotions to colors, influencing how they are perceived. For example, white symbolizes purity in Western cultures but is associated with mourning in Eastern cultures. Understanding these cultural differences is essential for artists and designers working in a global context. It ensures that their color choices resonate appropriately with diverse audiences.
Q: What are the advantages of using digital tools for color selection?
A: Digital tools offer an unlimited color paletteA color palette refers to a selection of colors used in design and art. It can set the tone, convey emotions, and highlight key elements. color wheel Types of Color Palettes • Monochromatic: Uses variations in lightness and saturation of a single color. Ideal for creating a harmonious and cohesive look. • Analogous: Combines colors that are next to each More and the ability to experiment freely without making permanent changes. They ensure consistent color application and provide features like layeringLayering is a fundamental technique in art that involves building up multiple layers of material to create depth, texture, and complexity in a composition. This approach is used in various art forms, including painting, drawing, digital art, and mixed media. Layering allows artists to add richness and dimension to their work, making it more dynamic and engaging. Defining Layering Layering More and special effects. Tools like digital color pickers and swatches help artists visualize color combinations. This enhances creativity and precision in the artwork.
Q: How does color affect user experience in digital media?
A: In digital media, color plays a significant role in user engagement and interaction. Colors can guide users’ attention, evoke emotions, and influence decisions. For example, red call-to-action buttons can create a sense of urgency. Effective use of color enhances the overall user experience and can lead to higher engagement and conversion rates.
Q: What is the role of color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More in branding?
A: Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More in branding focuses on how colors influence consumer perceptions and behaviors. Brands choose colors that align with their identity and message to evoke specific emotions. For example, blue is often used to convey trust and reliability, while red can stimulate excitement and urgency. Effective color choices help build a strong and memorable brand.
Q: How does color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More affect marketing strategies?
A: Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More plays a crucial role in marketing by affecting consumer emotions and decision-making. Marketers use colors strategically to attract attention, convey messages, and drive actions. For instance, yellow can grab attention and create a sense of happiness, while green often represents health and sustainability. Understanding these impacts helps create more effective marketing campaigns.
Q: What impact does color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More have on interior design?
A: In interior design, color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More is used to create specific moods and atmospheres within a space. Cool colors like blue and green can make a room feel calm and relaxing, while warm colors like red and orange can energize and stimulate. Designers choose colors based on the desired emotional effect and the room’s function. This thoughtful approach enhances the overall experience of a space.
Q: How does color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More relate to personality?
A: Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More suggests that the colors you prefer can reflect aspects of your personality. For example, people who favor blue might be seen as calm and trustworthy, while those who prefer red may be perceived as passionate and energetic. These preferences can influence choices in clothing, home decor, and even branding. Understanding this relationship can offer insights into personal and psychological traits.
Q: Why is blue significant in color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More?
A: Blue is often associated with calmness, trust, and reliability in color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More. It has a soothing effect and is frequently used in environments where relaxation and concentration are important, such as bedrooms and offices. In branding, blue is used by companies to evoke a sense of security and dependability. Its widespread use reflects its ability to convey a sense of peace and stability.
Q: How does color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More influence office decor?
A: Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More in office decor aims to create a productive and positive work environment. Blue and green are popular choices for their calming and focusing effects, while yellow can inspire creativity and optimism. The right colors can reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance overall productivity. Thoughtful color choices in office design contribute to a more efficient and pleasant workspace.
Q: What is a color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More chart?
A: A color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More chart visually represents how different colors can influence emotions and behaviors. It maps out various colors and their associated psychological effects, helping designers, marketers, and artists choose the right hues for their projects. These charts are useful tools for understanding the emotional impact of colors at a glance. They aid in making informed decisions about color use in various fields.
Q: How can color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More enhance an art project?
A: Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More can greatly enhance an art project by guiding the choice of colors to evoke specific emotions and reactions. Artists can use warm colors to create excitement and energy, or cool colors to convey calmness and serenity. Understanding the psychological impact of colors helps in crafting artworks that connect deeply with viewers. This approach adds an emotional layer to artistic expression.
Q: What are the psychological effects of color in art therapy?
A: In art therapy, colors are used to express emotions and facilitate healing. Warm colors like red and yellow can help release feelings of anger or frustration, while cool colors like blue and green can promote relaxation and peace. Art therapists use color choices to understand clients’ emotional states and guide them through the therapeutic process. The psychological effects of color play a vital role in achieving therapeutic goals.
Q: How can color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More be used in art therapy?
A: In art therapy, color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More is used to help clients express and understand their emotions. Warm colors can be used to explore feelings of anger or energy, while cool colors might help with relaxation and introspection. Therapists guide clients in choosing colors that reflect their current emotional state or desired outcomes. This process can facilitate healing and self-awareness.
Q: How do color meanings influence emotions in art?
A: Different colors have specific meanings that can evoke various emotions in art. For example, red can evoke feelings of passion or anger, while blue might induce calmness or sadness. Artists use these color meanings to enhance the emotional impact of their work. Understanding how colors affect emotions helps in creating more expressive and resonant artworks.
Q: How does color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More affect clothing choices?
A: Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More suggests that the colors you wear can influence how you feel and how others perceive you. For instance, wearing red can make you feel more confident and energetic, while blue can convey calmness and professionalism. Your color choices in clothing can reflect your mood, personality, and even social or cultural associations. Understanding these effects can help you select outfits that enhance your desired image and emotional state.
Q: How can color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More be applied in logo design?
A: In logo design, color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More helps create a brand identity that resonates with target audiences. Colors are chosen to evoke specific feelings and associations; for example, green can suggest eco-friendliness and health, while black can convey luxury and sophistication. Effective use of color in logos helps differentiate brands and communicate their values quickly. A well-chosen color paletteA color palette refers to a selection of colors used in design and art. It can set the tone, convey emotions, and highlight key elements. color wheel Types of Color Palettes • Monochromatic: Uses variations in lightness and saturation of a single color. Ideal for creating a harmonious and cohesive look. • Analogous: Combines colors that are next to each More can make a logo memorable and impactful.
Q: How do color moods affect art?
A: Color moods in art refer to the emotional tone set by the artist’s color choices. Warm colors like red, orange, and yellow can create a sense of warmth, excitement, or urgency. Cool colors like blue, green, and purple can evoke calmness, sadness, or introspection. By manipulating color moods, artists can guide viewers’ emotional responses and enhance the storytelling aspect of their work.
Q: What role does color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More play in creative color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More?
A: Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More is integral to creative color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More, which explores how colors interact and affect emotions. Understanding the psychological impacts of colors helps artists and designers create compositions that evoke specific feelings. This knowledge informs decisions on color harmony, contrast, and balance. Creative color theoryColor Theory is a comprehensive framework used to understand and analyze the use and interaction of colors in visual compositions. It serves as a critical guide for artists, designers, and marketers, helping them create harmonious and effective designs. This concept encompasses various principles and elements that dictate how colors are combined, perceived, and utilized. Primary Colors: • The three foundational More combines scientific insights with artistic intuition to enhance visual communication.
Q: How can color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More enhance an art project?
A: Color psychologyColor psychology examines how colors influence human behavior, emotions, and perceptions. This field combines elements of art, design, and psychology to understand the impact of color on our daily lives. It explores how different hues can evoke specific feelings and responses. Colors play a crucial role in visual communication. They can convey messages, set moods, and even affect decision-making. For More can greatly enhance an art project by guiding the choice of colors to evoke specific emotions and reactions. Artists can use warm colors to create excitement and energy, or cool colors to convey calmness and serenity. Understanding the psychological impact of colors helps in crafting artworks that connect deeply with viewers. This approach adds an emotional layer to artistic expression.
You might also enjoy reading the following posts by Pigment Pool:
The History of Color Theory: Must-Know Facts for Creatives
Mastering Art with Color Theory: Kandinsky’s Transformative Vision
Ultimate Guide to the Best Colored Pencils – Must-Know Facts for Hobbyists and Artists
A Brief History of Colour Pigments
Understanding Chinese Art: Colors and Their Cultural Significance
The Art of Hanging Art: How to Follow and Break Rules
The Best Acrylic Paint Set for Artists and Hobbyists In 2022
The Best Sketching Pencils for Artists and Beginners in 2022
This article may contain compensated links. Please read Disclaimer for more info. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
